There are several UPS parallel solutions, which are briefly sorted out here for your reference. It mainly reveals the principle and analyzes the advantages and disadvantages.
Here is the order from high-end (HIGH) to low-end (LOW).
1. Modular parallel + external static switch mode
This is the current relatively high, large, and upper model, which costs more money, let's look at the structure first:
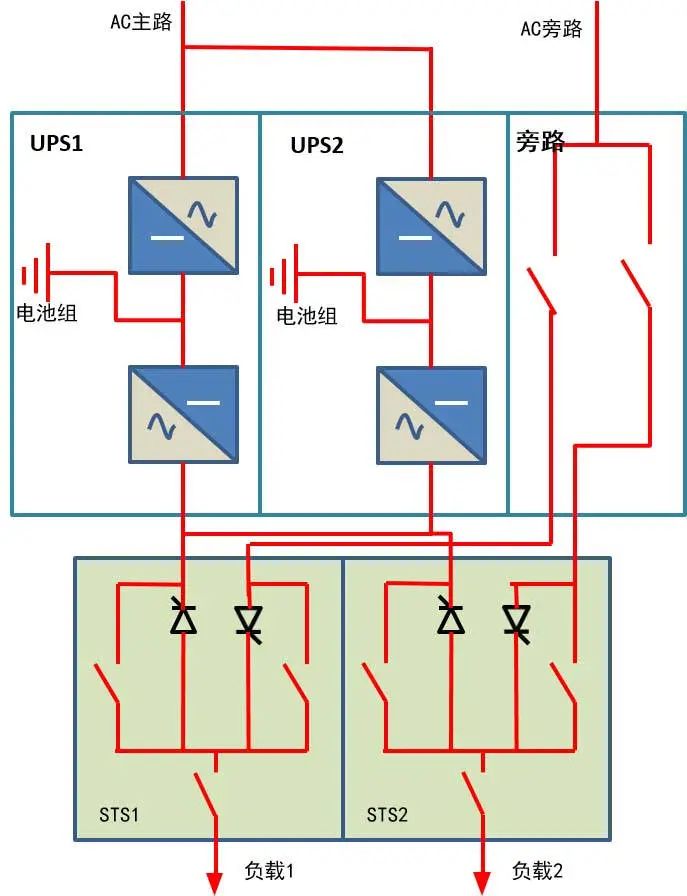
Merit:
After any UPS fails and shuts down, the load can be borne by the remaining UPS;
When working normally, the load is shared by all UPS, and the load rate is low;
Independent STS static switch is set up, and STS maintenance bypass is provided for easy maintenance, which improves the reliability of STS faults and reduces risk points.
The load can also be distributed and configured to reduce the risk factor.
Shortcoming:
There are many additional equipment, 2 UPS, 2 STS, and 1 mains power distribution cabinet, which requires a large area and a large investment;
2. Parallel UPS hot backup system
This is the most commonly used mode at present, although the cost is not low, but the reliability is worth the price, all the most commonly used parallel methods, if you want to save some money, then use the 2+1 parallel method: three UPS parallel, any failure, will not affect the normal power supply.
The following is the schematic diagram of the 1+1 parallel:
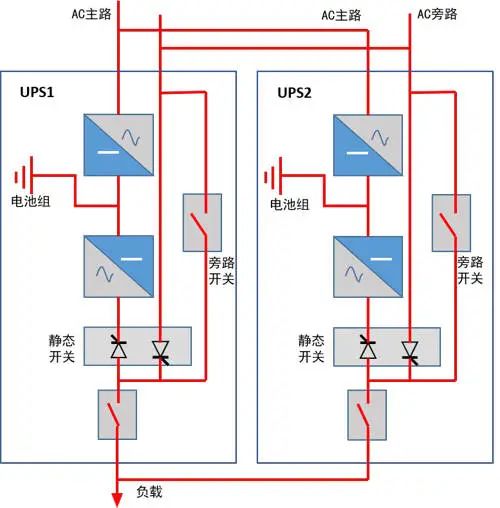
Merit:
After any UPS fails and shuts down, the load can be borne by the remaining UPS;
When working normally, the load is shared by all UPS, and the load rate is low;
When the mains power is stopped, the battery life is the cumulative time of all battery packs;
Shortcoming:
The technical requirements are high and the debugging is complex, requiring the brand, model and specifications of the parallel UPS to be completely consistent;
The output synchronization of each UPS is high, and once the circulation is generated out of sync, it may lead to short circuit failure.
3. Bypass UPS hot backup system
The bypass UPS redundancy mode is a hot standby mode, that is, only one UPS is used to provide power to the load at the same time, and the other is waiting, and once the running main UPS fails, the waiting UPS immediately takes over the load. The principle is as follows:
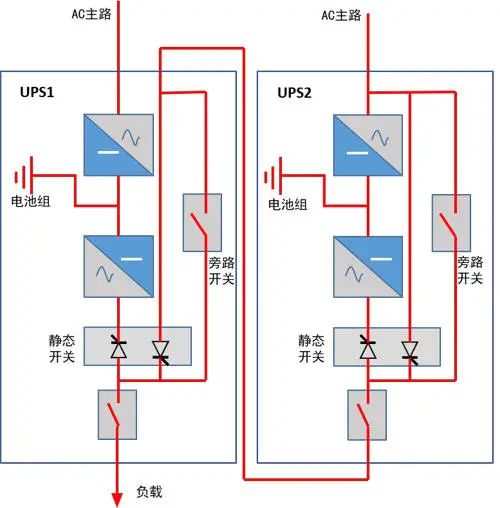
Merit:
It is easy to realize the later transformation, and UPS of different brands and capacities can be formed;
It can be maintained separately, and the load is still protected by UPS during maintenance.
The operating efficiency is higher than that of tandem UPS;
When the mains power is stopped, the battery life is the cumulative time of the two battery packs;
Shortcoming:
The static bypass switch of UPS1 is a bottleneck in the system, and once it fails, it may cause the load to lose power.
UPS2 long-term no-load operation, low efficiency; And the battery pack cannot be discharged for a long time, and its life is reduced;
4. Tandem UPS hot backup system
Tandem UPS is a redundancy mode adopted by the early redundancy mode due to the backwardness of UPS technology, which is no longer in use, and its principle is as follows:
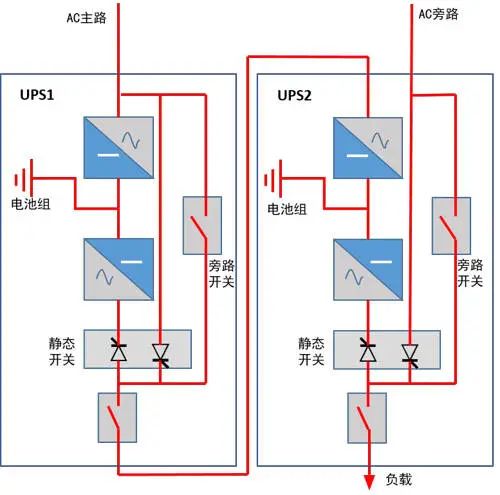
Merit:
After any UPS fails and shuts down, the load can be borne by the remaining UPS;
When working normally, the load is shared by all UPS, and the load rate is low;
Independent STS static switch is set up, and STS maintenance bypass is provided for easy maintenance, which improves the reliability of STS faults and reduces risk points.
The load can also be distributed and configured to reduce the risk factor.
Shortcoming:
There are many additional equipment, 2 UPS, 2 STS, and 1 mains power distribution cabinet, which requires a large area and a large investment;
5. Stand-alone online UPS
The parallel redundancy mode is listed earlier, and finally let's take a look at the principle of UPS stand-alone:
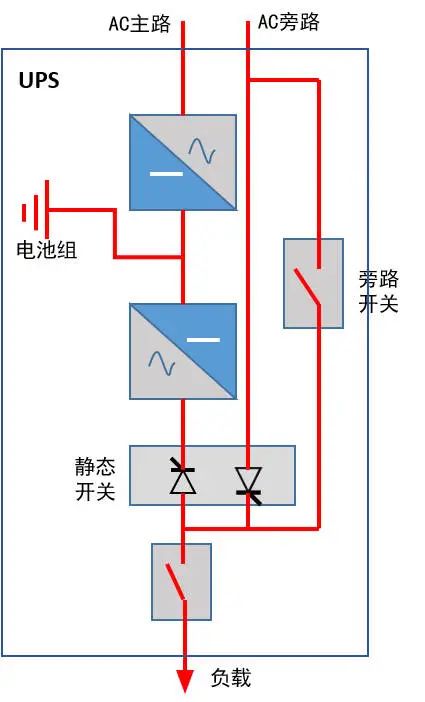
Merit:
The system architecture is simple, the control logic is easy to implement, and the cost is low.
Shortcoming:
Static bypass switches are the bottleneck of the system, and once the failure may cause the load to lose power;
Power outage is required when the whole machine needs to be replaced (it can be solved by adding an external bypass);
During maintenance, switch to bypass mains power supply, and the load is not protected;
Summary:
At present, the most commonly used method is method "2"; Users with higher requirements adopt method "1"; In practical applications, it is also commonly used in the method "3", and it is only in the system upgrade, it turns out that the old UPS can work normally, it is a pity to discard it, what should I do? Then act as a "hot standby" to power the bypass of the new UPS (the bypass is in a non-power waiting state when the UPS is running normally).
As the old saying goes: what suits you is right, choose a good UPS, choose a good redundancy method, please choose a balance between reliability and price according to your actual needs.

