How data centers are designed to be fireproof
3.1 Park planning
(1) Fire spacing
The fire prevention measures of multiple data centers are mainly to increase the spacing between buildings. Fire spacing mainly refers to preventing fire-burning buildings from igniting adjacent buildings within a certain period of time. The fire spacing specified in the specification is shown in the figure below: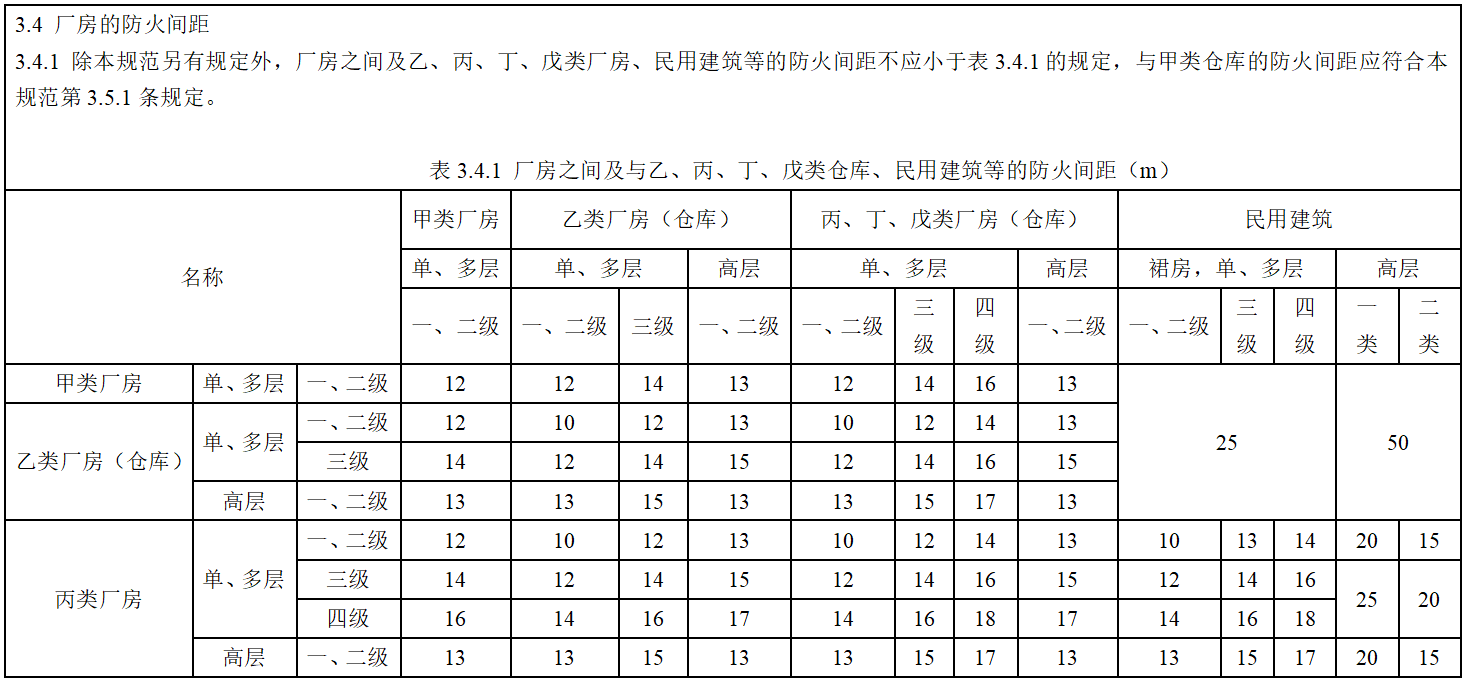
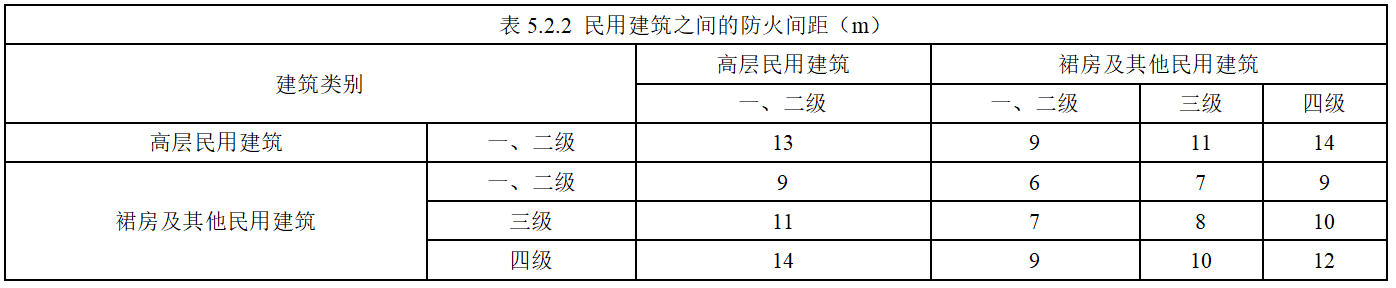
(2) Oil storage tank
Control fuel flash point (Class C), capacity and total reserves, buried directly underground. The minimum distance between the buried oil tank and the building is as follows: The minimum distance between the building and the park road when the capacity of a single tank is not more than 50 cubic meters and the total reserve is not more than 200 cubic meters is as follows:
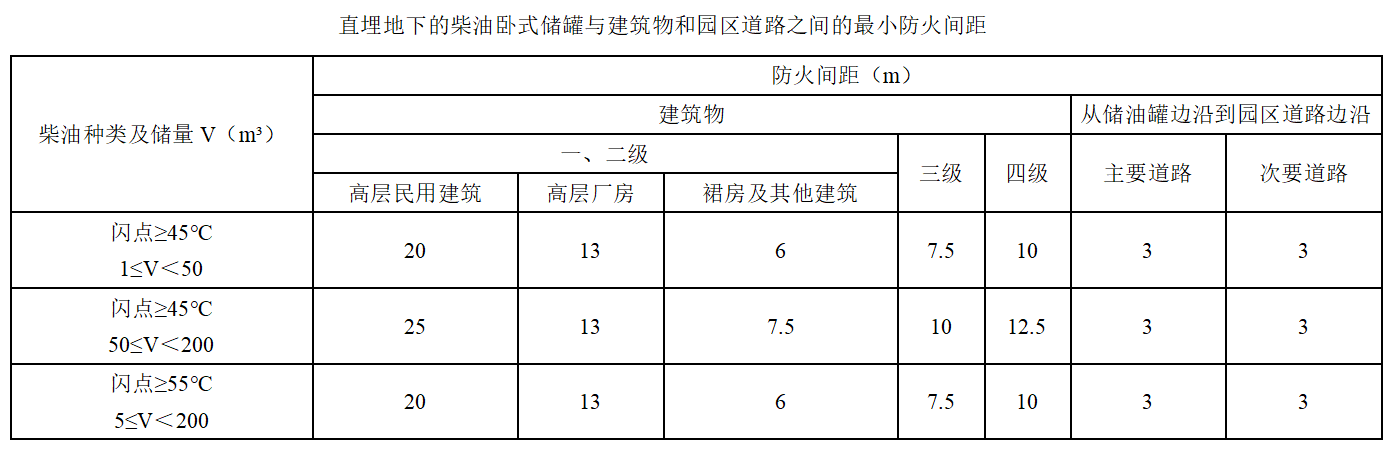
For buried oil tanks larger than 200m³, the group arrangement meets the spacing of not less than 20 meters.
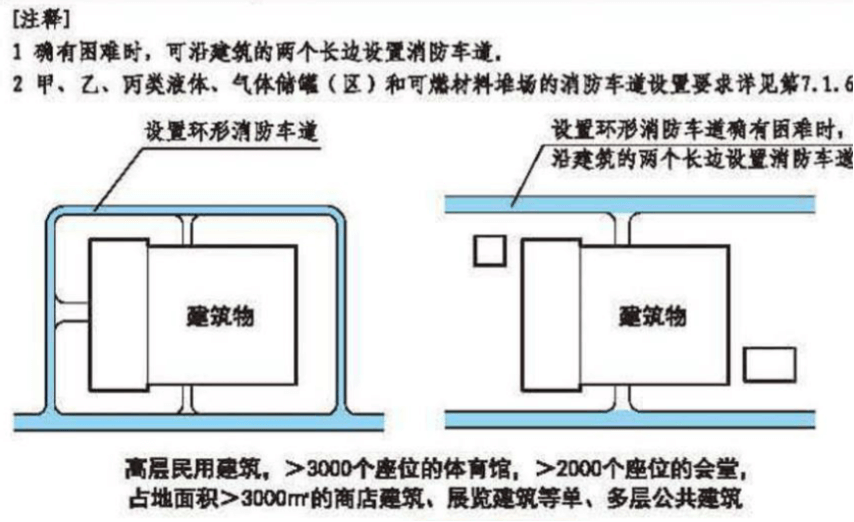
(3) Fire lanes
Class C factories, high-rise civil buildings, and high-rise industrial buildings covering an area of more than 3,000 square meters should be equipped with circular fire lanes.
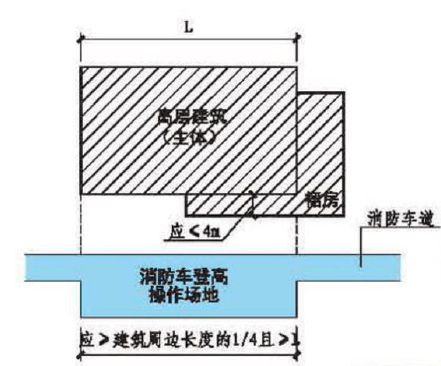
High-rise buildings should be equipped with fire truck climbing sites along at least one long side or 1/4 of the circumference and not less than one long side.
3.2 Building fire resistance
Fire resistance limit: the time taken when the building components are subjected to fire to the loss of bearing capacity, integrity and thermal insulation.
The fire resistance level of the data center should not be lower than Level 2.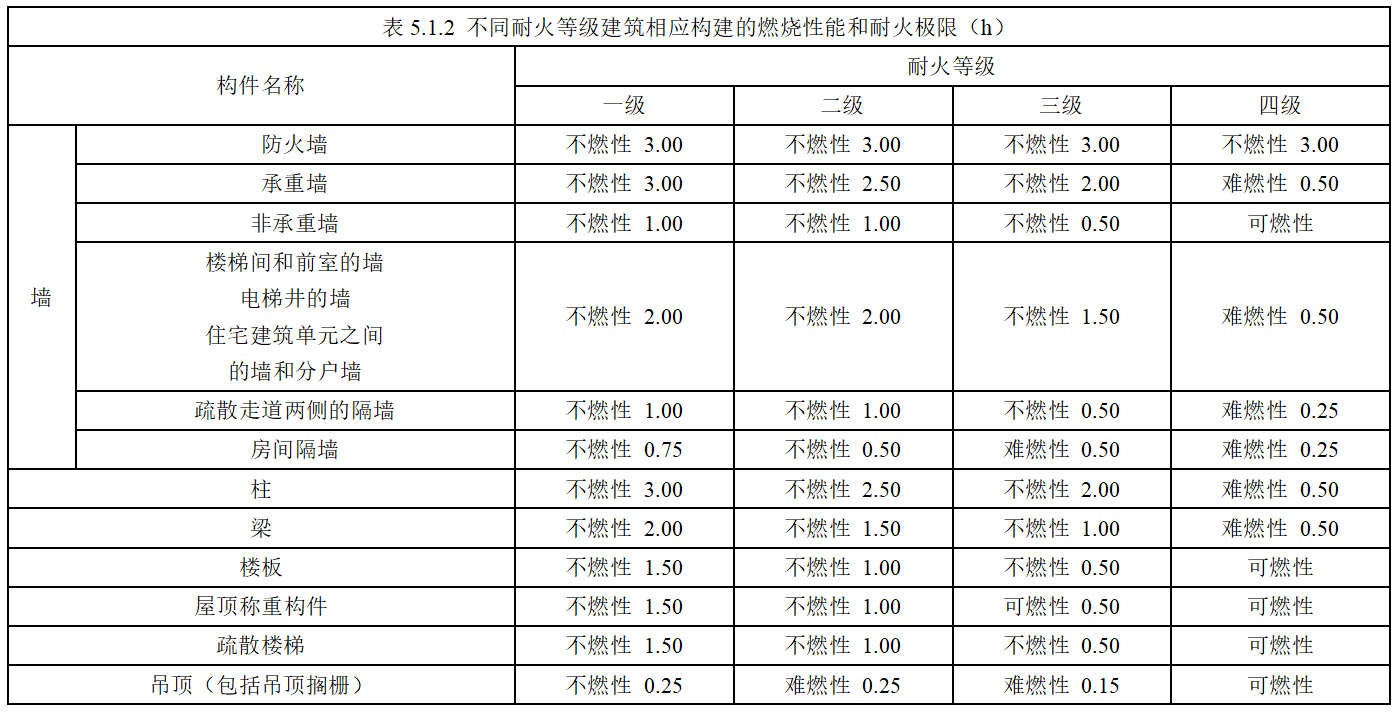
3.3 Fire prevention of building interior decoration
The roof, siding and partitions of the main room of the data center shall be non-combustible (Class A) and shall not be made of organic composite materials. The floor and other decoration should be made of decoration materials not lower than (flame retardant) B1 grade. When the data center is in the same building as other functional buildings, the data center and other functional buildings in the building should be separated by a fireproof partition wall with a fire resistance limit of not less than 2.0h and a floor slab of 1.5h, and the door on the partition wall should be opened with a Class A fire door.

From the General Code for Building Fire Protection GB55037-2022, it can be seen that the wall ceiling of the front room, stairwell, power distribution room, fire pump room and other equipment rooms should be made of Grade A materials. The provisions of the code are as follows:
6.5.3 The combustion properties of the ceiling, wall and floor interior decoration materials of the following parts shall be class A:
1. Evacuation corridors, evacuation floors, and evacuation rooms;
2. Evacuate the stairwell and its front room;
3. The front room of the fire elevator or the front room of the shared room.
6.5.4 The combustion performance of the floor decoration materials of the fire control room shall not be lower than B1 level, and the combustion performance of the interior decoration materials of the ceiling and wall shall be class A. The combustion performance of the ceiling, wall and floor interior decoration materials of the following equipment rooms should be class A:
1. Fire fighting equipment room such as fire pump room, mechanical pressurized fan room, smoke exhaust machine room, fixed fire extinguishing system cylinder room, etc.;
2. Power distribution room, oil-immersed transformer room, generator room, oil storage room;
3. Ventilation and air conditioning machine room;
4. Boiler room.
The setting area image is shown below:

For the interior wall painting materials of stairwells and front rooms, Article 3.0.6 of the Fire Protection Code for Building Interior Decoration Design stipulates that inorganic decoration coatings applied to Grade A substrates can be used as Class A decoration materials; Organic decoration coatings applied to Grade A substrates with a wet coating ratio of less than 1.5kg/m² and a coating dry film thickness of not more than 1.0mm can be used as B1 decoration materials. Inorganic decoration coatings are applied to A-grade substrates to meet A requirements. Therefore, if the roof and interior walls of the traffic core and equipment room of all buildings are painted, "inorganic decoration paint" should be selected.
Therefore, for the use of coatings:
1. All public spaces such as traffic core foyers, equipment rooms, and underground garages must use inorganic decoration coatings;
2. For public buildings, almost all buildings must use inorganic decoration coatings for the ceiling and part of the wall.
3.4 Fire protection zoning in the building
One effective way to stop the spread of fire in a building is to divide fire zones within the building.
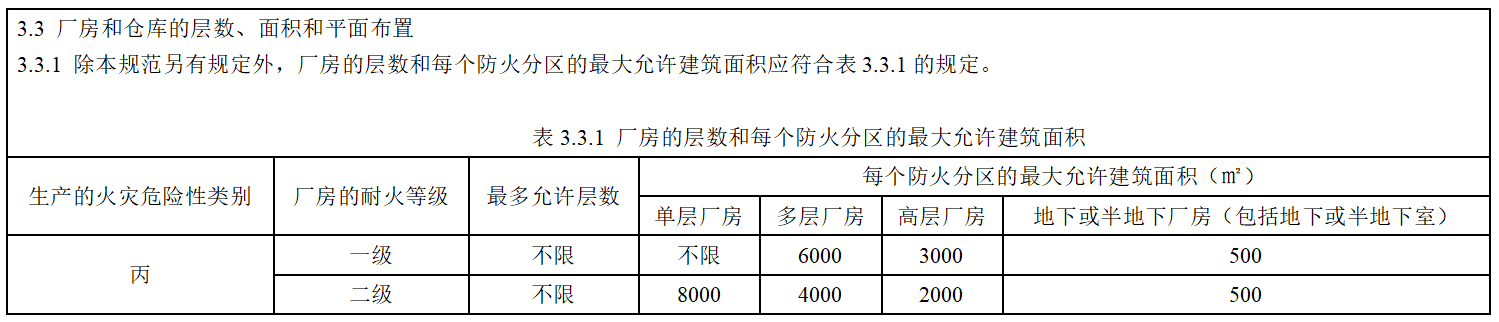
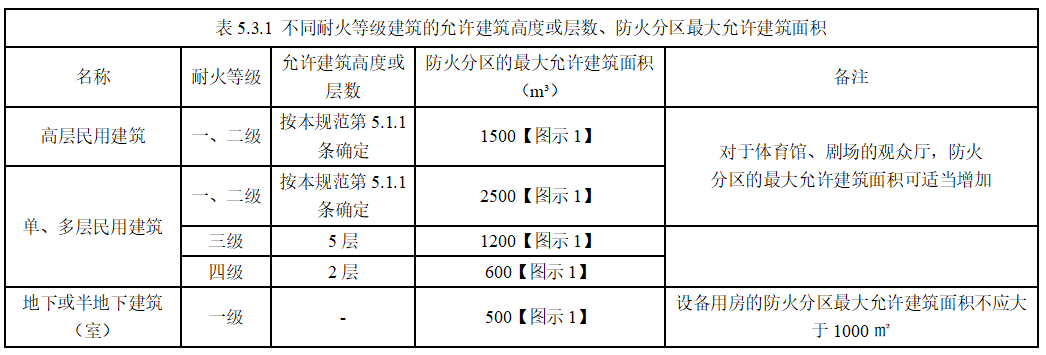
The fire protection zone area in the building is shown in the table below:
(1) Fire protection zone area of industrial buildings: (When an automatic fire extinguishing system is installed in the building, the fire protection zone area can be doubled.) )
Fire protection zone area of civil buildings: (When an automatic fire extinguishing system is installed in the building, the fire protection zone area can be doubled.) )
3.5 Building evacuation design
When a building catches fire, one of the key points in the design of the building evacuation is that the safety exits (stairs, first floor doors) are close enough.
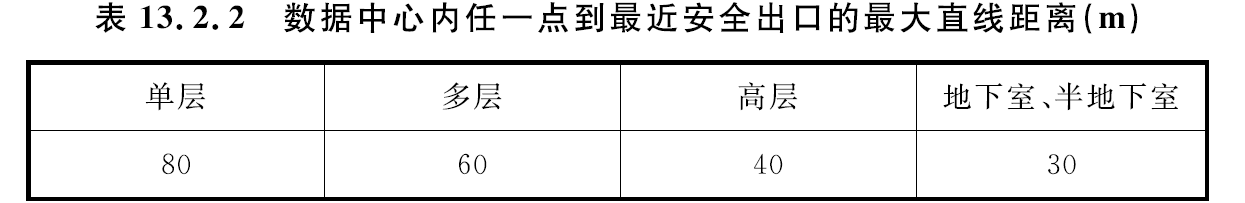
When the data center is designed according to the factory, the fire hazard classification of the data center should be classified as Class C, and the straight-line distance from any point in the data center to the nearest safety exit should not be greater than the provisions of Table 13.2.2. When the main engine room is equipped with a highly sensitive aspirated smoke detection fire alarm system, the straight-line distance from any point in the main room to the nearest safety exit can be increased by 50%.
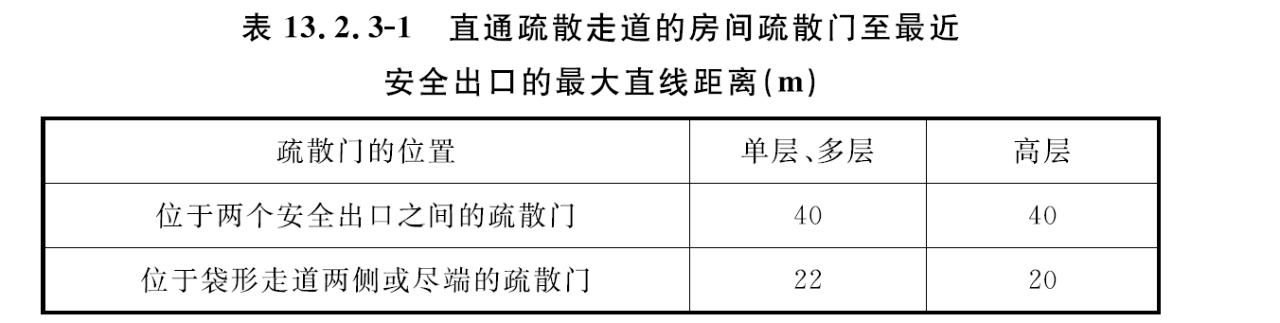
When the data center is designed according to civil buildings, the straight-line distance from the evacuation door of the room directly to the evacuation corridor to the nearest safety exit shall not be greater than the provisions of Table 13.2.3-1, and the straight-line distance from any point in each room to the evacuation door of the room directly to the evacuation walkway shall not be greater than the provisions of Table 13.2.3-2. When all automatic fire extinguishing systems are used in the building, the safe evacuation distance can be increased by 25% in areas with automatic sprinkler fire extinguishing systems.
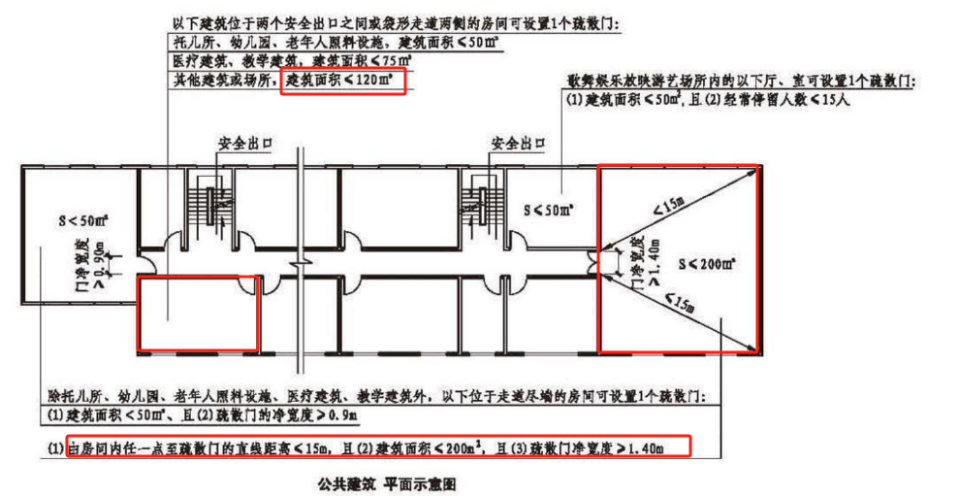
For the main computer room with a construction area of more than 120 square meters, there should be no less than two evacuation doors, and they should be arranged in a dispersed manner. A main machine room with a construction area of not more than 120 square meters or a main computer room located at the end of the bag-shaped walkway with a construction area of not more than 200 square meters, and the straight-line distance from any point in the computer room to the evacuation door is not more than 15m, an evacuation door can be set up, and the net width of the evacuation door should not be less than 1.4m. The evacuation door of the main computer room should be opened in the direction of evacuation, should be automatically closed, and should be guaranteed to be opened from the computer room under any circumstances. Corridors and stairwells should be unobstructed, and there should be obvious evacuation signs.
3.6 Structural fire protection design
(1) Reinforced concrete materials and masonry materials
According to different fire resistance levels, structural components are required to have different combustion properties and fire resistance limits. The details are shown in the figure below:
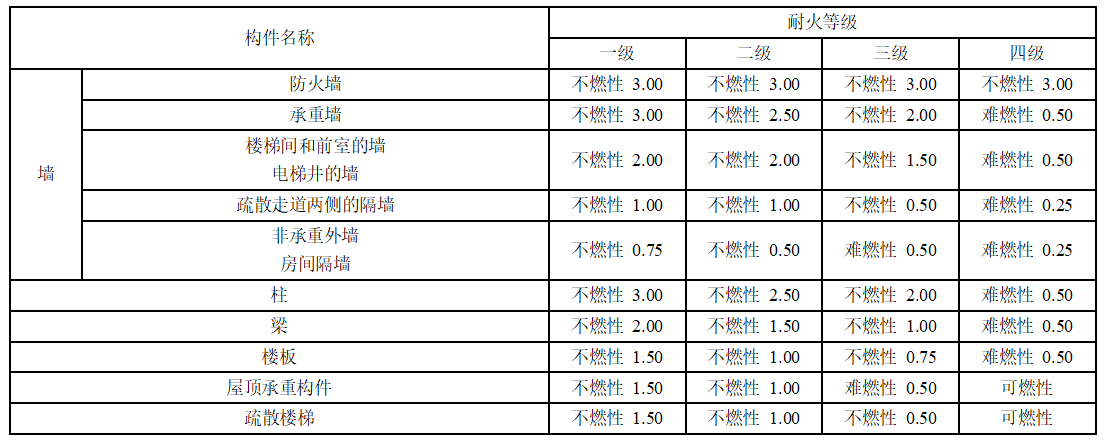
The combustion performance and fire resistance limit of concrete materials and masonry materials are shown in the following figure:
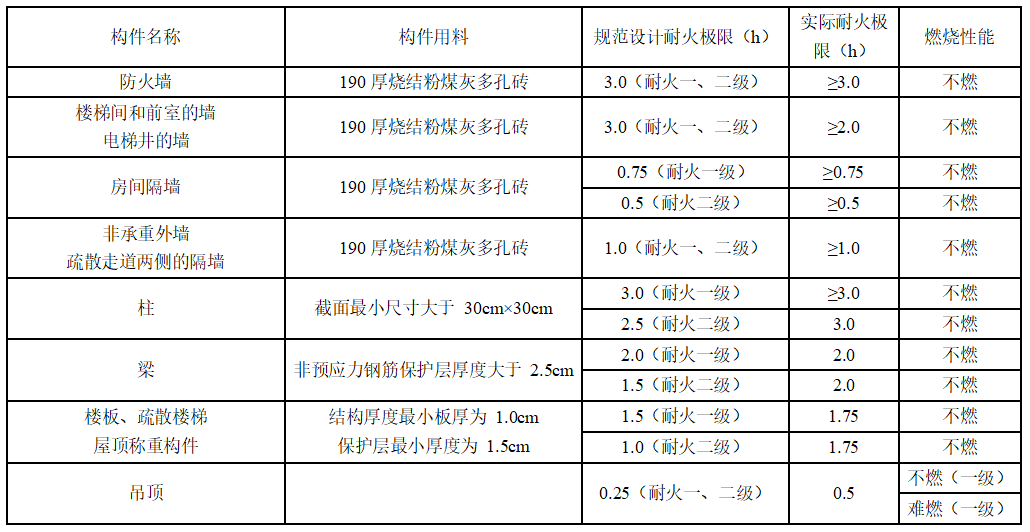
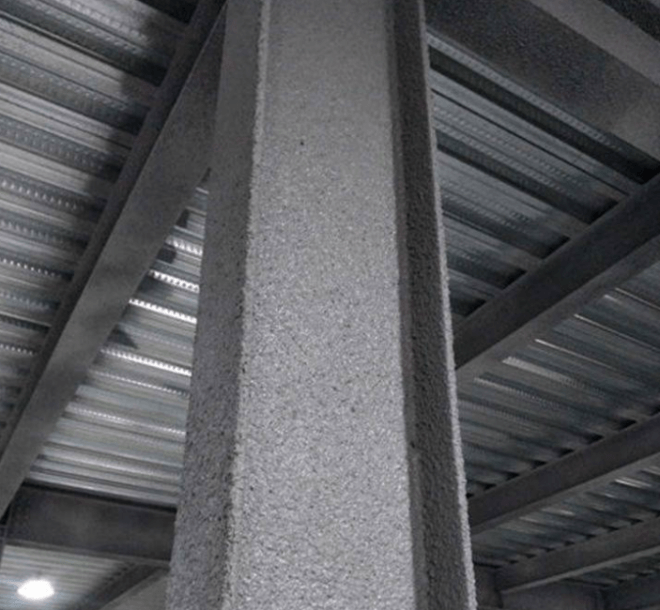
(2) Steel structure fire protection
1. Fireproof design: The steel structure should be calculated and designed according to the limit state of the structural refractory bearing capacity. The refractory limit method, bearing capacity method or critical temperature method can be used. In layman's terms, it is to calculate the fire resistance time not less than the design refractory time, calculate the bearing capacity of the component under fire not less than the design load, or the maximum temperature of the component under fire is not higher than the critical temperature of the component to achieve the fire protection of the steel structure to meet the design requirements.


2. Fire protection measures and structural measures: one or several combinations of the following measures can be adopted: spraying (plastering) fireproof coatings, covering fireproof plates, covering flexible felt insulation materials, outlying concrete, metal mesh mortar or masonry. For indoor hidden components, non-intumescent fireproof coatings should be selected; for components with a design fire resistance limit greater than 1.5h, intumescent fireproof coatings should not be selected. The thickness of the non-intumescent fireproof coating layer should not be less than 10mm. Intumescent products are made of organic resins, blowing agents, etc.; non-intumescent products are made of flame-retardant or non-combustible inorganic insulation materials. Intumescent products will expand when fired, and are insulated and fire-proof through the expanded hollow carbonaceous layer; Non-intumescent products do not expand when fired, and are insulated and fireproofed through their own thermal insulation coating. Generally, the fire resistance of inflatable products is 1-2 hours, and non-intumescent products are 2-3 hours.

3.7 Electrical fire protection design
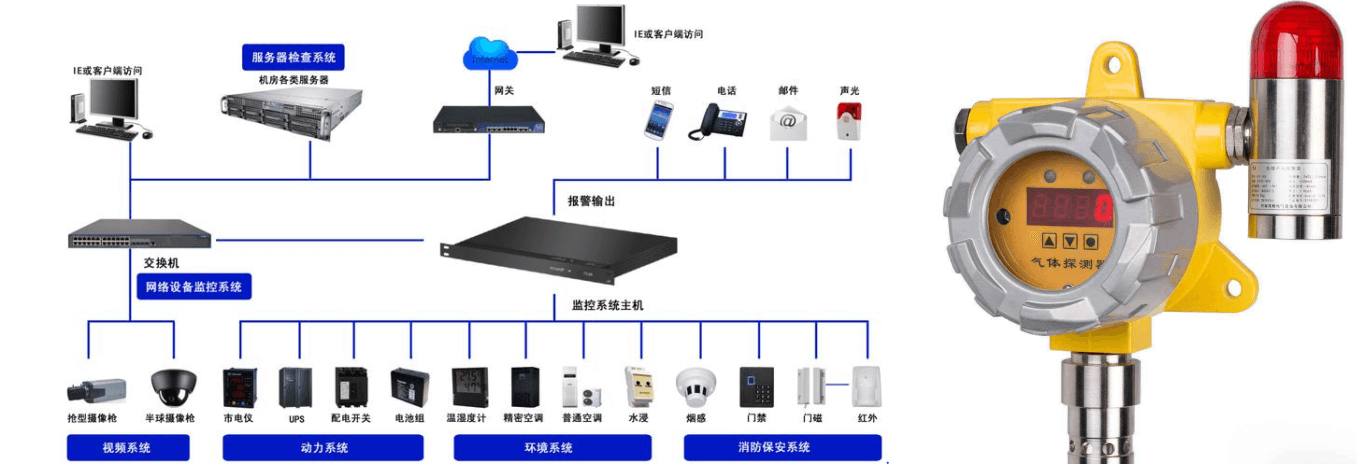
The main electrical fire prevention measures are: The data center will set up a power environment monitoring system in the computer room, and monitor the status of distribution cabinets, UPS cabinets, air conditioners and other equipment in real time through modules and sensors, and find problems in time and notify relevant personnel to deal with them. Set up combustible gas detectors in the oil storage room to monitor the concentration of combustible gases in the air in real time.
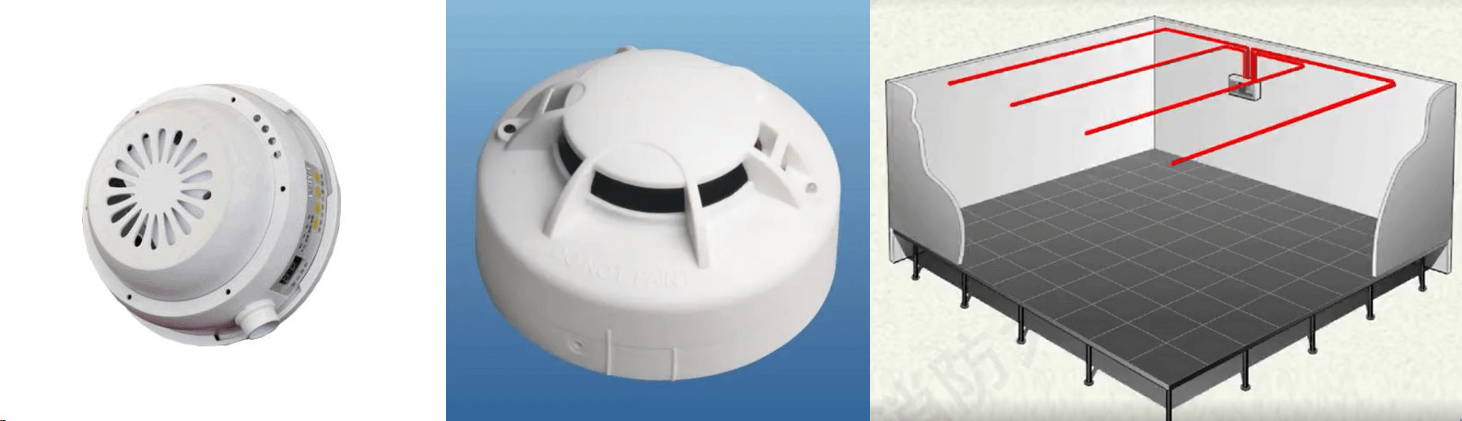
Install smoke and temperature sensing fire detectors: They can detect both smoke and temperature changes, and need to be installed high or in the middle of the room to be able to detect smoke and temperature changes. A suction smoke detector in the computer room is a device capable of identifying and alarming at the early stages of a fire It monitors tiny smoke particles in the air through very sensitive optical sensors. This system works by taking an air sample and analyzing the smoke particles in the sample to detect any possible fire.
Set up fire power monitoring, monitor the AC or DC power supply (including main and backup) power supply of fire protection equipment When overvoltage, undervoltage, lack of phase, overcurrent, or interrupted power supply fault, the fire power monitor conducts sound and light alarms and records, sets up electrical fire monitoring, collects, analyzes, and judges information on electrical parameters such as residual current in electrical lines and equipment, and at the same time sends out alarm signals and stores and prints alarm information and other basic functions.
3.8 Lightning protection design
Grounding system: The data center should establish a complete grounding system, including working grounding, protective grounding and lightning protection grounding. The grounding resistance should comply with relevant regulations to ensure that the lightning current can be smoothly introduced into the ground. The grounding wire should have sufficient cross-sectional area and insulation compressive strength, and should adopt a design of multiple backups and mutual redundancy to ensure the stability and reliability of the system
Lightning protection equipment: Data centers should be equipped with lightning protection equipment such as lightning rods, lightning protection belts, and lightning protection nets to prevent damage to buildings and equipment caused by direct lightning strikes. The specifications and models of lightning protection equipment should comply with relevant standards and regulations, and should also have certificates of conformity and test reports.

Lightning protection: Data centers should adopt multi-level lightning protection measures, including lightning protection for power systems and signal lines. Each forms a complete lightning protection system. For important equipment and lines, stricter lightning protection measures should be taken that should be coordinated with each other, such as installing surge protectors.
Lightning protection detection and maintenance: Data centers should regularly conduct lightning protection testing and maintenance, check the grounding resistance, working status of lightning protection equipment, etc., to ensure the reliability and effectiveness of lightning protection systems. Problems and faults found should be repaired and dealt with in a timely manner to avoid affecting the normal operation of the data center.

3.9 Anti-static design
Flooring: The floor of the data center should have static conductive properties, which can effectively release and conduct static electricity. The floor can be anti-static flooring or electrostatic conductive movable flooring, and the material should have sufficient mechanical strength and chemical stability. The surface resistance value of the floor should comply with relevant regulations to meet the requirements of anti-static.
Wall: The wall of the data center should be made of materials that are not easy to generate static electricity, such as antistatic coatings. At the same time, the walls should be dustproof to maintain a clean and good working environment.

Equipment: The equipment in the data center should have a grounding function that can direct static electricity underground. The shell of the equipment should be made of electrostatic conductive materials to prevent static electricity from accumulating on the surface of the equipment. The grounding resistance value of the equipment should comply with relevant regulations to ensure that static electricity can be smoothly introduced underground.
Personnel: Data center workers should wear anti-static overalls and anti-static shoes to prevent damage to equipment caused by human electrification. At the same time, staff should conduct regular anti-static training to understand anti-static knowledge and operating procedures.

Humidity control: Data centers should maintain an appropriate humidity range, generally 40%-60%. Excessive humidity can cause damage to the equipment, while low humidity can easily cause static accumulation.
Monitoring system: The data center should establish a complete electrostatic monitoring system to monitor and record the static electricity situation in each area in real time, and take timely measures to deal with abnormal situations once they are found.
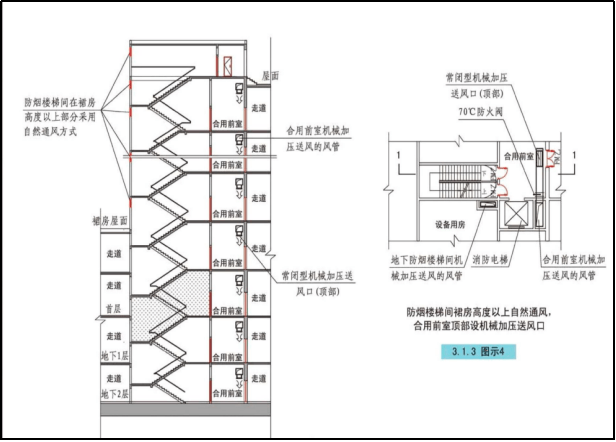
3.10 Smoke-proof design
The smoke-proof stairwell and its front room, the front room or shared front room of the fire elevator room, the evacuation area and connecting walkways in the evacuation floor, the evacuation room, the evacuation walkway, the special fire passage, etc. are all safe evacuation and rescue channels in the event of a fire in the building. In the event of a fire, the smoke can be discharged by opening the exterior windows and other natural smoke exhaust facilities, or the smoke prevention facilities with mechanical pressurized air supply can be used to prevent the smoke from invading the evacuation channel or evacuation safety area.

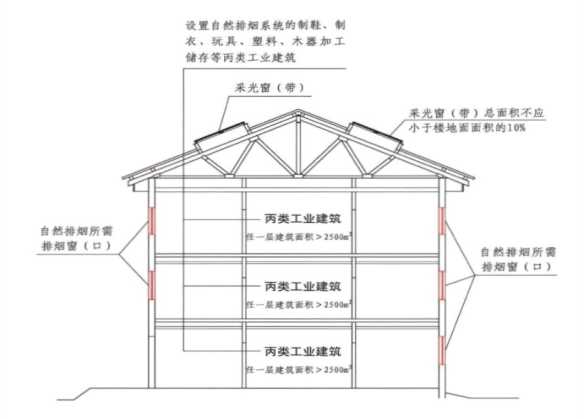
3.11 Smoke exhaust design
In addition to places that are not suitable for setting up smoke exhaust facilities and places with slow fire development, the following places or parts of industrial and civil buildings should adopt smoke exhaust and other flue gas control measures: above-ground Class C production sites with a construction area of more than 300 m² and frequent people staying or many combustibles, and above-ground rooms with a construction area of more than 300 m² and frequent people staying or combustibles; Except for the high-temperature production process, other above-ground Class D production sites with a construction area of more than 5000m²; underground or semi-underground D production sites with a construction area of more than 1000m²; above-ground Class C warehouses with a construction area of more than 300m²; Evacuation corridors with a length of more than 20m in factories or warehouses with a building height of more than 32m, evacuation walkways with a length of more than 40m in other factories or warehouses, and evacuation walkways with a length of more than 20m in civil buildings.

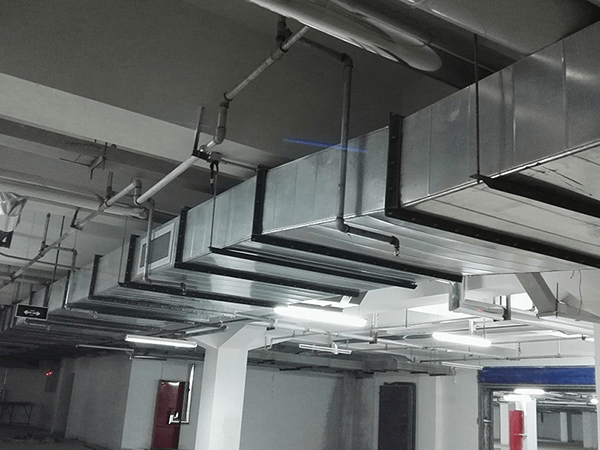
3.12 Fireproof design of equipment
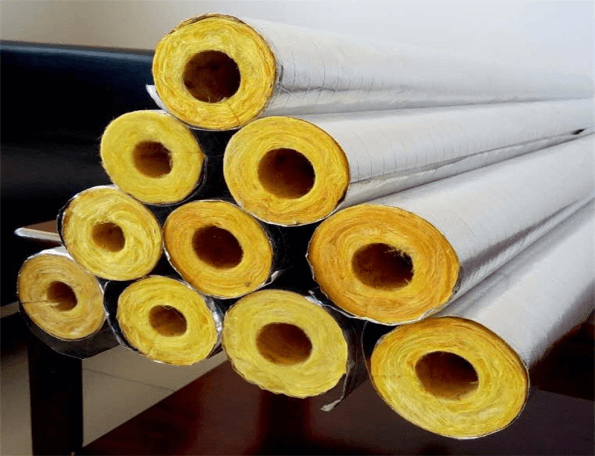
The machine room should be made of non-combustible or flame-retardant materials, and the combustion performance of the materials should comply with the relevant provisions of the GB50222-1995 "Fire Protection Code for Building Interior Decoration Design". The Code for Fireproof Design of Buildings 9.3.14 stipulates that the air ducts of ventilation and air conditioning systems should be made of non-combustible materials, usually galvanized steel plates. Flame retardant materials are used as the material of the air duct, usually composite air ducts, in order to ensure that the overall performance of the composite air ducts reaches Class A non-combustible. 9.3.15 It is stipulated that the insulation materials of equipment and air ducts should be non-combustible materials; Humidification materials, anechoic materials and binders used in humidifiers should be made of non-combustible materials, and flame-retardant materials can be used when it is really difficult.



