To meet the 1.5°C range of the Paris Climate Agreement, there is an urgent need to take measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from industry. President Xi Jinping proposed at the 75th session of the United Nations General Assembly on September 22, 2020: our country's carbon dioxide emissions will strive to peak before 2030 and strive to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060.
With the promotion of the "East Data and West Computing" strategy and the "construction of eight computing power hubs", ultra-large data centers have grown rapidly, with a compound annual growth rate of more than 45%. At the same time, the electricity consumption and carbon dioxide emissions of data centers are growing rapidly, attracting more and more attention from governments at all levels and the whole society. According to CDCC data, the national data center electricity consumption in 2021 will be 93.7 billion kWh, accounting for 1.13% of the total electricity consumption of the whole society (the National Bureau of Statistics data is higher, nearly twice the CDCC data), and is expected to reach 120 billion kWh by 2025, with carbon dioxide emissions of about 78.3 million tons, accounting for 0.77% of the national carbon dioxide emissions, and is expected to reach 100 million tons by 2025.
In this context, the improvement of energy efficiency, the use of renewable energy, and waste heat recovery in data centers have attracted great attention from the industry. Among them, for the waste heat recovery and utilization of data centers, a large number of relevant national standards, specifications and policies put forward requirements for it.
-
The "Energy Saving Design Standard for Public Buildings" (GB 50189-2015) points out that in areas where there is available waste heat or industrial waste heat, waste heat or industrial waste heat should be used as a heat source.
-
The Data Center Design Code (GB 50174-2017) points out that when designing the air conditioning system of the data center, the economic benefits of natural cooling and waste heat recovery should be calculated separately, and the energy-saving design scheme with the greatest economic benefits should be adopted.
-
The "Technical Rules for Green Data Center Building Evaluation" issued by the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development points out that when there is a demand for heating or domestic hot water in the auxiliary area of the data center and the surrounding area, it is advisable to design a comprehensive energy utilization plan to recover the exhaust heat of the main engine room air conditioning system as a heat source, and it is advisable to use a heat pump unit to recover and exhaust the heat.
-
The "Guiding Opinions on Strengthening the Construction of Green Data Centers" jointly issued by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the State Administration of Organ Affairs, and the National Energy Administration proposes to encourage the construction of clean energy utilization systems such as natural cold sources, waste heat recovery and utilization of its own systems, or renewable energy power generation in its own places.
-
The "Guiding Opinions on Strengthening Energy Conservation and Emission Reduction in the Information and Communication Industry in the 13th Five-Year Plan" issued by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology proposes to promote the application of advanced technologies and products such as green intelligent servers, natural cooling sources, waste heat utilization, and distributed energy supply.
-
The National Development and Reform Commission issued the "Implementation Plan for the National Integrated Big Data Center Collaborative Innovation System Computing Power Hub", which proposes to promote the adoption of energy-saving technology models such as high-density integrated and high-efficiency electronic information equipment, precision air conditioning in new computer rooms, liquid cooling, cabinet modularization, and waste heat recovery and utilization in data centers.
The clustering of large-scale and ultra-large data centers, and even large-scale data centers in core areas, has created more favorable conditions for large-scale, efficient, low-cost, and long-distance transmission of waste heat utilization projects. This white paper will summarize and prospect the waste heat recovery and utilization technology schemes of large and ultra-large data centers and their clusters.
1. Waste heat utilization of the air conditioning system of the chilled water machine room
The refrigeration process of the air conditioning system of the chilled water room is as follows: the chilled water pump brings the heat in the computer room to the cold evaporator through the water circulation, the compressor transfers the heat absorbed by the evaporator to the condenser under the electric drive, the cooling water pump pushes the water circulation to exchange the heat of the condenser and bring it to the cooling tower, and the cooling tower dissipates the heat in the circulating water to the outdoor environment through forced heat exchange through direct or indirect means, and so on.
The air conditioning system of the chilled water machine room usually has low energy efficiency throughout the year, and generally adopts the waste heat recovery of the chilled water side, and the system principle is as shown in the figure below (Figure 1). Waste heat recovery mainly occurs in winter, and heat recovery is carried out through waste heat recovery units to heat the surrounding buildings.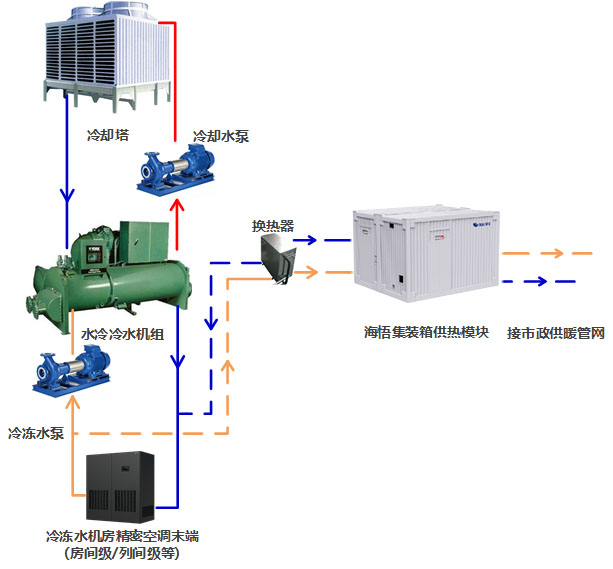
Fig.1 Heating principle of waste heat recovery on the chilled water side of the computer room
2. Waste heat recovery from the return air of the AHU air conditioning system room
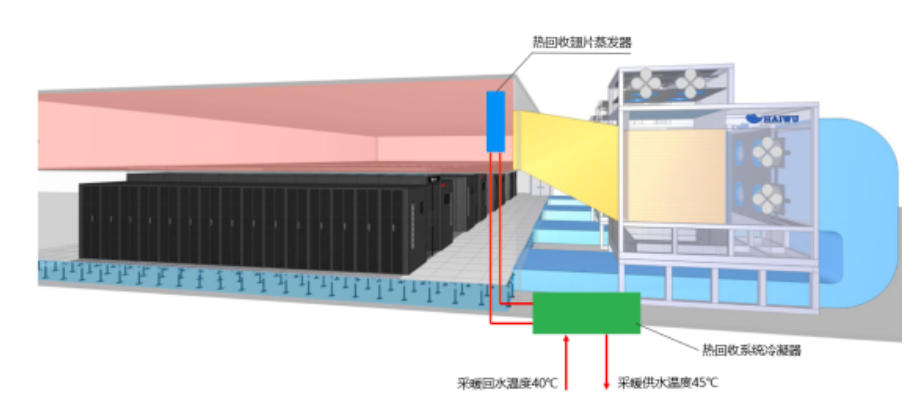
AHU air conditioning system is a temperature control method widely used by large data center data centers, especially in the northern region, which can make full use of the natural cooling source and greatly reduce the PUE of year-round operation. The rest of the heat recovery principle is shown in the figure below (Fig. 2), the 38°C hot air from the machine room flows through the evaporator of the heat pump unit added for waste heat recovery, and the temperature is reduced to 26~28°C, where the heat grade is higher and the recovery effect is the best. Then, the air-air heat exchanger in the AHU unit is exchanged with the outdoor air, and the AHU can automatically adjust the outdoor cold air entering the air-air heat exchanger according to the indoor return air temperature.
(Fig. 2a) Principle of return air waste heat recovery in the computer room of AHU air conditioning system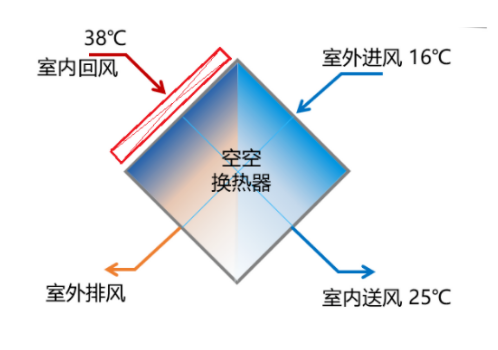
(Fig. 2b) Waste heat recovery energy flow diagram of the return air in the computer room of the AHU air conditioning system
According to the calculation of the operating parameters of AHU products of Haiwu Group, as long as the fin evaporator is installed in the return air cavity of the computer room, the temperature of the return air inlet and return heat evaporator is 38 °C, and the temperature of the evaporator is 26~28 °C, and the usable temperature can reach more than 10 °C, and the maximum wind resistance of the fin is only about 40 Pa. The total power consumption of AHU fans increased by about 0.85kW, but the operating COP of Haiwu waste heat recovery heat pump under this condition can reach more than 6.31, so that the unit energy consumption of 45°C hot water in all seasons can be reduced to less than 1/6 of traditional electric heating equipment.
3. Heat recovery of Haiwu PHU all-weather energy-saving unit
PHU units were born under the pressure of the policy of "strict control of PUE and WUE", and have genes of saving, efficiency enhancement and environmental friendliness in their bones. Among them, the PHU model with heat recovery produced by Haiwu is a newly launched "energy technology and information technology integration product" in 2022, which is to promote the development of the industry in the right direction with the goal of "building a green and low-carbon data center", demonstrating the unyielding attitude of Haiwu people towards the waste heat recovery and utilization of data centers!
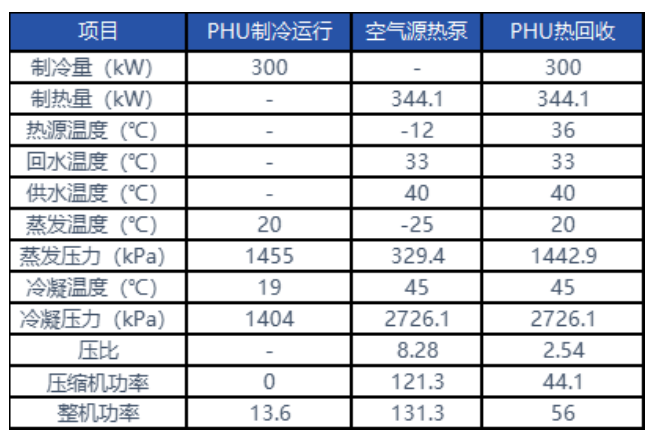
In the winter heating season, the PHU heat recovery unit can maintain a higher evaporation temperature, using a small pressure ratio compressor to produce heat energy with ultimate efficiency, and the heat energy efficiency of the whole machine is significantly improved compared with the air source heat pump unit, which can be explored from the following comparison table:
Integrate data center cooling and office area heating to maximize the comprehensive utilization of energy. The principle is as shown in the figure below (Fig. 3), a heat recovery module is connected in parallel to the compressor exhaust pipeline, which controls the flow direction of heat through a solenoid valve, recovers exhaust heat, and provides heating hot water. The heat supply of the whole machine is adjusted by solenoid valve and electric ball valve. The A/B system is graded to cut in/out of the heat recovery condition to avoid violent fluctuations in water temperature.
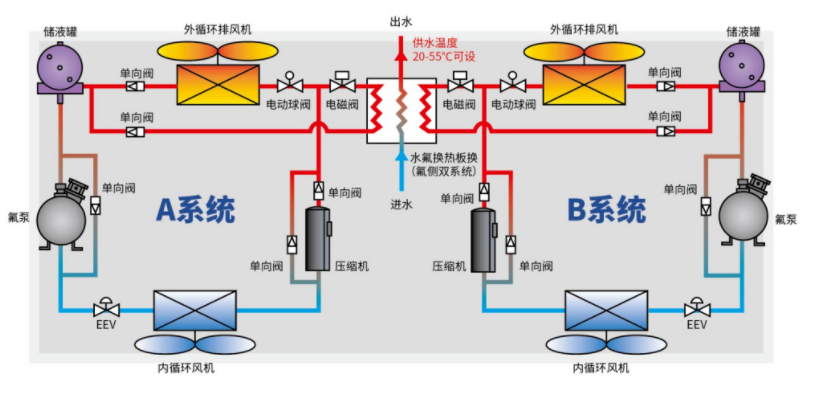
Fig.3 Principle of heat recovery PHU integral fluorine pump unit
The common characteristics of the waste heat recovery technologies and products of the data center shown above are: the proportion of waste heat recovery and utilization in the total annual heat discharge is still very low, and the form of heat utilization is low-temperature hot water, and the use is also limited to washing, heating, breeding, printing and dyeing...... and other smaller fields. Due to the extremely limited transmission radius of low-temperature hot water, it is generally constrained by the pipe network and pumping costs, and can only cover the range of 2-3 kilometers, and the location of the data center has special needs, and there is a high probability that there is a lack of suitable heat users in the surrounding area, resulting in the outreach of both supply and demand, and the situation is quite embarrassing.
4. Expansion of the heating radius of waste heat recovery
Saved and recovered energy are the most "green" energy. The total amount of waste heat in the data center is extremely large, and the distance between the target demand side is far away, breaking through the transportation bottleneck between supply and demand, which has become a top problem to overcome.
How to expand the heat range?
At present, compared with the waste heat of power plants, chemical waste heat, and waste heat of heat companies, the reference heat price of about 50 °C is 50-60 yuan/GJ, and the main consumption objects of heat are: community heating, bulk hot water users (such as printing and dyeing plants), cash crop planting greenhouses, etc. The distance between these three customers and IDC is uncontrolled, and the problem of heat transfer must be solved first to establish a connection between supply and demand. Generally, heat pipeline transportation at around 50°C is only suitable for distances within a radius of 2-3km, while other transfer methods need to be considered for longer distances.
To sum up, the heat cost of several central waste heat recovery heat we proposed is extremely low, and the difference between the market heat price is large, and there is room for integration into the intermediate transfer and operation links. Connecting the heat source and the user with wheels becomes a feasible way to expand. At present, Haiwu people are focusing on the implementation of this plan, and examples can be used to confirm the feasibility of this approach in the future. The following figure (Fig. 4 and Fig. 5) is the schematic diagram of the phase change regenerative vehicle to extend the heating range:

Fig. 4 Phase change heat storage vehicles connect heat sources with users and increase employment
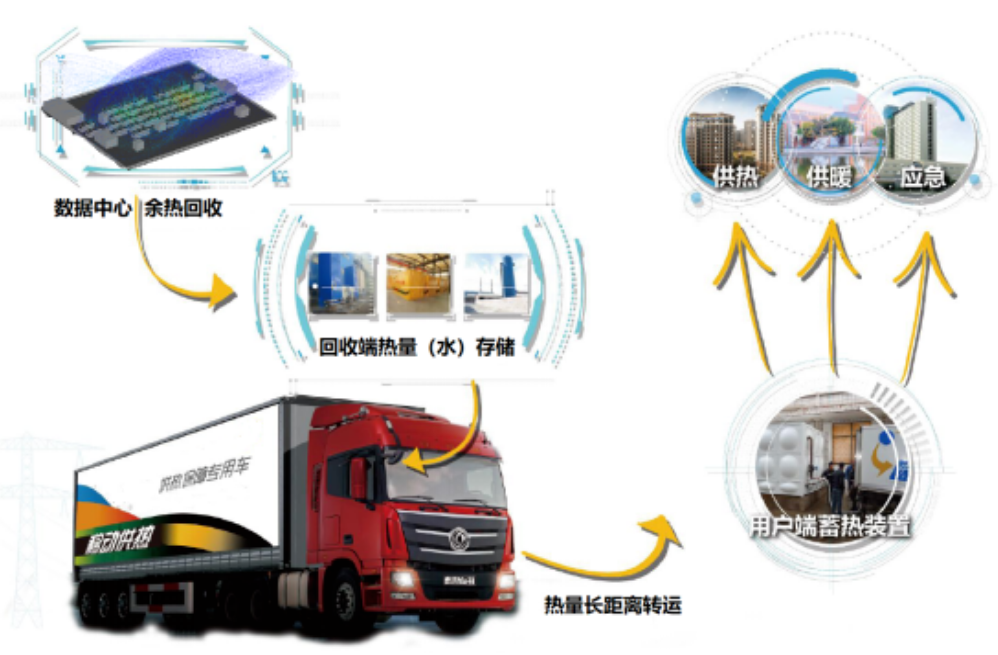
Fig.5 Heat transfer expands the range of heat utilization
5. Temperature range expansion of waste heat recovery
Industrial steam heat pump technology has matured and is powered by electricity, a high-energy cross-cutting technology that provides process heat to replace most fossil fuels for industrial process heating.
As can be seen from the energy flow diagram, the process heat generated by the heat pump is the sum of the input heat from the electrical energy input and the waste heat source, and the heat output is usually 2 to 5 times that of the electrical energy input. Haiwu's high-temperature steam heat pump can be closely integrated with the heat recovery heat pump system in the PHU heat recovery unit and AHU air conditioning system, based on the massive and stable low-temperature heat source provided by the super-large data and its cluster, to produce high-grade industrial steam, and transport it to industrial and commercial users with a radius of 15 kilometers through the pipeline network, which is a win-win situation and a very high economic value for the waste heat of the data center (Figure 6 and Figure 7):
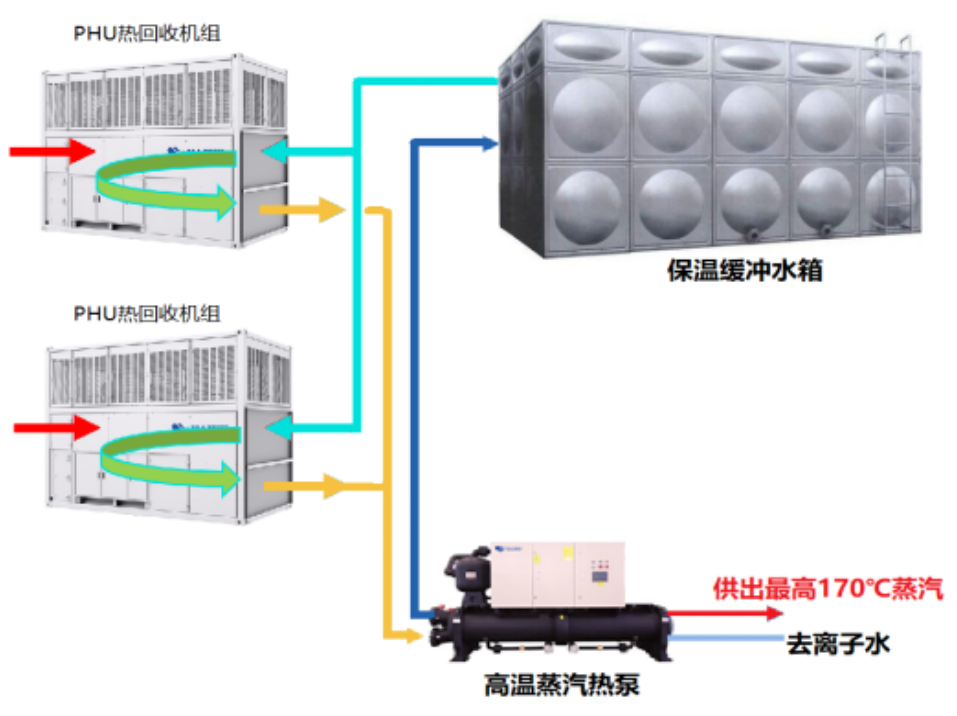
Fig.6 Steam supply system using PHU heat recovery unit
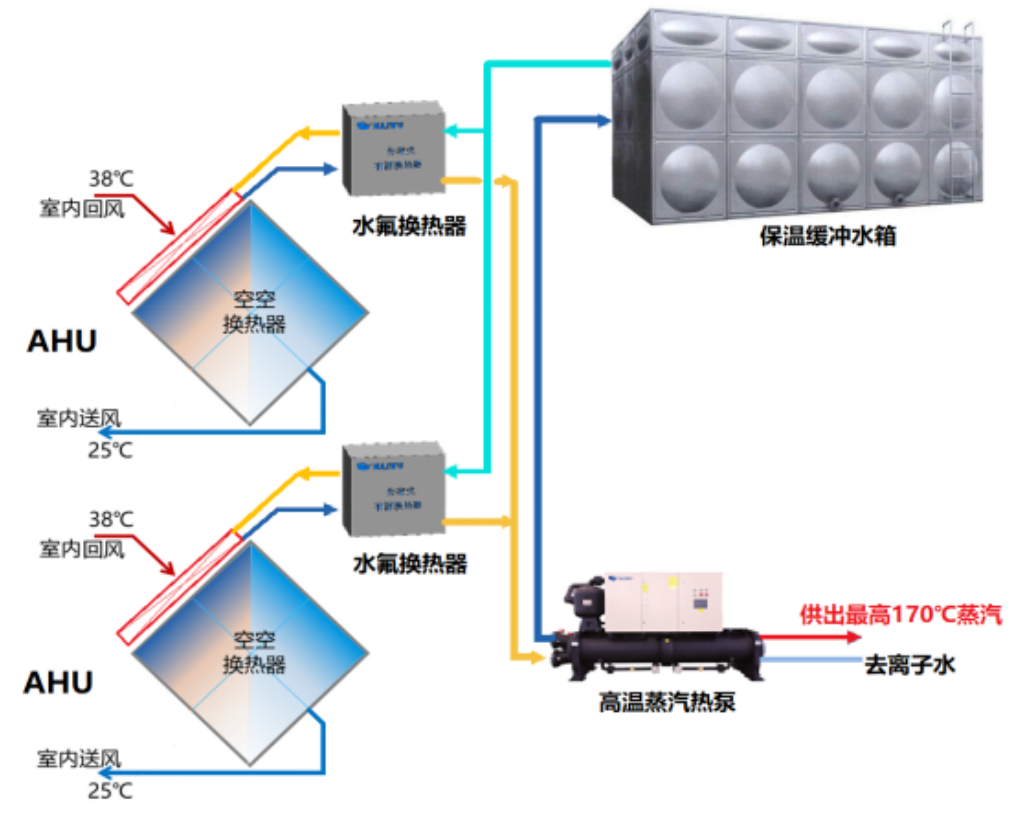
Figure 7 Steam supply system in a data center using AHU for heat dissipation
Examples have proved that this method can bring a bright prospect of "industrial symbiosis". In Appenzell, Switzerland, waste heat from a data center is used as a heat source for a high-temperature heat pump that is used for process heat, hot water, and building heating at a neighboring cheese plant. This saves about 1.5GWh of natural gas per year for the mountain cheese plant.

