Abstract: According to the data released by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, in 2019, the total scale of data center racks in our country exceeded 2.26 million, and the electricity consumption exceeded 130 billion kWh, accounting for about 2% of the electricity consumption of the whole society. In 2020, the state put forward the goal of "carbon neutrality": "Strive to peak carbon dioxide emissions before 2030 and strive to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060." It is a carbon neutrality requirement put forward by the whole society, and data centers are no exception, no matter how different the emission reduction paths and methods, for data centers, the first step is to calculate the overall energy consumption and carbon emissions, and the national standards for data center energy consumption and greenhouse gas emission accounting methods have not yet been promulgated, this issue is discussed, and relying on national norms, referring to authoritative databases at home and abroad, through formula derivation, data collation, to get the data center The annual comprehensive energy consumption and carbon emission accounting methods, and the accounting and comparison of a data center project by scenario.
Key words: data center; integrated energy; carbon emissions; carbon accounting; carbon neutrality; carbon peaking; gas generator sets; 3. Joint supply
introduction
In recent years, China's social economy has undergone tremendous changes, and the country's strength has continued to grow. According to "GDP" as the ranking parameter, China has surpassed Japan to become the world's second largest economy after the United States. However, before we took an extensive development path of competing for resources, manpower, high investment, high consumption, and high emissions, which overdrew China's environment and resources. It is particularly surprising that China has now surpassed the United States as the largest emitter of greenhouse gases. Greenhouse gas emissions are a sensitive issue of global concern due to rapid changes in the global climate, which in turn leads to the deterioration of the ecological environment.
At the United Nations General Assembly in September 2020, the leader said that China will increase its nationally determined contributions, strive to peak carbon dioxide emissions by 2030, and strive to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060; In December of the same year, leaders further announced a series of new initiatives to increase their NDCs at the Climate Ambition Summit to mark the fifth anniversary of the Paris Agreement.
According to the "Research Report on the Development of China's "New Infrastructure", from a global perspective, data centers will account for the largest share of global energy consumption by 2025, up to 33%. From our country's point of view, the power consumption of global data centers has grown by more than 12% for eight consecutive years. As one of the few industries where energy consumption accounts for a continuous increase in the proportion of total electricity consumption in society, it is of great significance for data centers to actively practice carbon neutrality.
Carbon neutrality refers to the total amount of greenhouse gas emissions directly or indirectly generated by enterprises, groups, projects or individuals within a certain period of time, and offset their own carbon dioxide emissions through afforestation, energy conservation and emission reduction.
Regardless of the difference in emission reduction paths and methods, for data center projects, the first step is to calculate the overall carbon emissions, and how to scientifically and correctly calculate the carbon emissions and standard coal content of data center projects has become the first problem to be solved.
1. Comprehensive energy consumption of data centers
Nowadays, the cloud era is booming, new infrastructure is accelerating, in the context of the whole society further promoting energy conservation and emission reduction, energy conservation and consumption reduction has become the common goal of the government and the data center industry, the use of energy in data centers is multifaceted, not only exists in the purchased electricity, standby diesel generator operation of diesel combustion carbon dioxide, domestic water, air conditioning water consumption consumption - water also needs to be calculated into the comprehensive energy consumption and carbon emissions.
At present, our country is focusing on optimizing the energy structure, taking the development of clean and low-carbon energy as the main direction of adjusting the energy structure, insisting on the development of non-fossil energy and the efficient and clean utilization of fossil energy at the same time, gradually reducing the proportion of coal consumption, increasing the proportion of natural gas consumption, and greatly reducing energy consumption emissions. Due to the heat loss in the power generation process, the thermal efficiency of conventional thermal power plants in our country is usually less than 40%. The development of cascade utilization technology of thermal energy can significantly improve energy utilization, such as gas-steam combined cycle thermoelectric cooling triple power generation system, which considers the load demand of electricity, refrigeration, hot water and other loads to realize the cogeneration technology of producing electricity, heat energy and cooling, and the comprehensive energy efficiency can be as high as 90%; A data center project in a science and technology park located in Changping District, Beijing, has adopted a gas triple power supply unit, burning natural gas to generate electricity, and using waste heat to be cooled by a lithium bromide unit to replace the mains power all the way to reduce carbon dioxide emissions.
1.1 Purchased electricity consumption
The annual power consumption of the data center can be calculated according to the number of cabinets, the power of a single cabinet, and the average annual PUE value of the data center project, and the calculation formula is as follows:
1.2 Energy consumption working fluid - water consumption
The water consumption of the data center includes the water consumption of the air conditioning system and the water consumption of office life, the water consumption of the air conditioner can be estimated at the consumption of 0.3m3 of water per cabinet per day, and the office water consumption can be estimated at 40L per person per day, and the calculation formula is as follows:
1.3 Diesel consumption
Data centers mostly use 10kV diesel generator sets with a basic power of 2000kW, according to the empirical value, each unit consumes 500 liters of diesel per hour, based on the monthly maintenance and overhaul operation of each diesel generator for 30 minutes, each diesel generator runs for 6 hours per year, so the annual diesel consumption of the data center can be calculated, the calculation formula is as follows:
1.4 Natural gas consumption
According to the mainstream gas generator products in the market, every 1m3 of natural gas can generate 4kWh of electricity, and at the same time, 4kW of cooling capacity is recovered to estimate the natural gas consumption, the formula is as follows: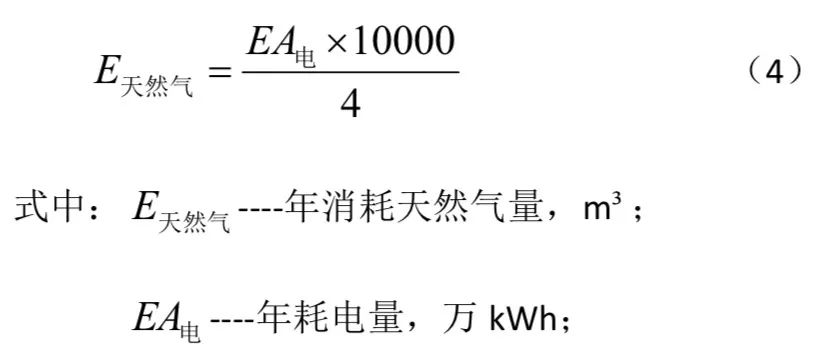
1.5 Comprehensive energy consumption calculation
According to the mainstream gas generator products in the market, every 1m3 of natural gas can generate 4kWh of electricity, and at the same time, 4kW of cooling capacity is recovered to estimate the natural gas consumption, the formula is as follows:
The calculation of comprehensive energy consumption of data centers is mainly based on the requirements of GB/T2589-2020 "General Principles for Comprehensive Energy Consumption Calculation", and the calculation formula is:
The standard coal coefficient can refer to the parameters in Appendix A and Appendix B of GB/T2589-2020 "General Principles for the Calculation of Comprehensive Energy Consumption", and the total comprehensive energy consumption of the data center can be obtained according to the total amount of different energy consumption and its corresponding discounted coal coefficient.
The commonly used coefficient of discounted coal is shown in Table 1:
Table 1 Commonly used coefficient of discounted coal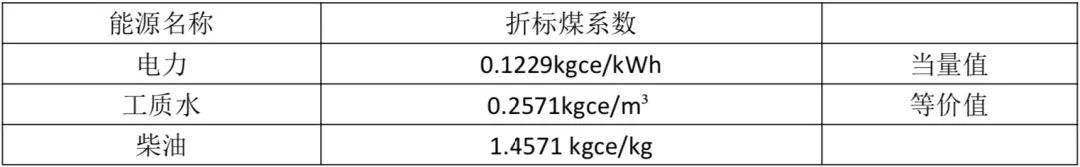
2. Data center carbon emission accounting
According to relevant international standards, the division of corporate emission reduction responsibilities can be divided into three categories: Category 1 is the most direct, mainly referring to direct emissions; Scope 2 mainly includes the emissions generated by the electricity and steam consumption of enterprises, because electricity or heat needs to be purchased from public utilities, and the carbon emissions in this process do not occur within the physical boundaries of the enterprise, so they are indirect emissions. Category 3 mainly refers to other arrangements related to the production and operation of enterprises, and its boundaries are not very clear, involving the industrial chain, including products purchased upstream and sold downstream. In general, data centres only consider Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions when considering carbon emissions.
2.1 Carbon emissions of purchased electricity
For the calculation of carbon emissions of data centers, because the current standard GB/T 32151 "Greenhouse Gas Emission Accounting and Reporting Requirements" does not include the data center industry, according to the requirements of ISO14064-1:2018 "Greenhouse Gases - Part 1: Specification for Clear Quantification and Reporting of Greenhouse Gas Emissions at the Organizational Level", and GB/T 32151.1- The calculation method of 5.2.4 "Emissions from purchased electricity" in the 2015 "Greenhouse Gas Emission Accounting and Reporting Requirements Part 1: Power Generation Enterprises" is calculated. At the same time, this is also a more conventional method for the accounting of carbon emissions in the corporate social responsibility report (ESG) of our country enterprises, and the calculation method is as follows:
2.2 Carbon dioxide emission factors
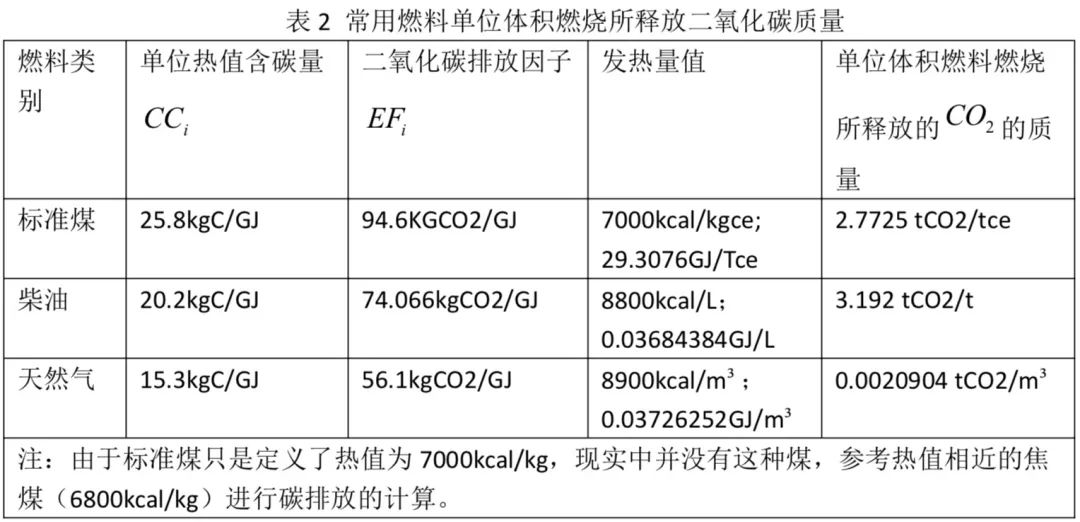
According to Equation (6), when the total energy consumption is multiplied by the corresponding emission factor, the carbon dioxide emissions are obtained, referring to GB/T 32151.1-2015 "Greenhouse Gas Emission Accounting and Reporting Requirements - Part 1: Power Generation Enterprises", Section 5.2.2.3 "Emission Factor Data Acquisition" calculation formula is as follows:

3. Calculate the example
Based on the situation of a data center project in Guangdong Province, the project adopts the purchased power scheme and the weather power generation plan for comprehensive energy consumption calculation and carbon emission accounting, and the basic information of the project is as follows:
3.1 Accounting for the use of purchased electricity schemes
According to Equations 1 to 7, the project is comprehensively calculated and carbon emission accounted, and the calculation results are as follows:
Table 4 Comprehensive energy consumption calculation and carbon emission accounting of the project (mains power supply)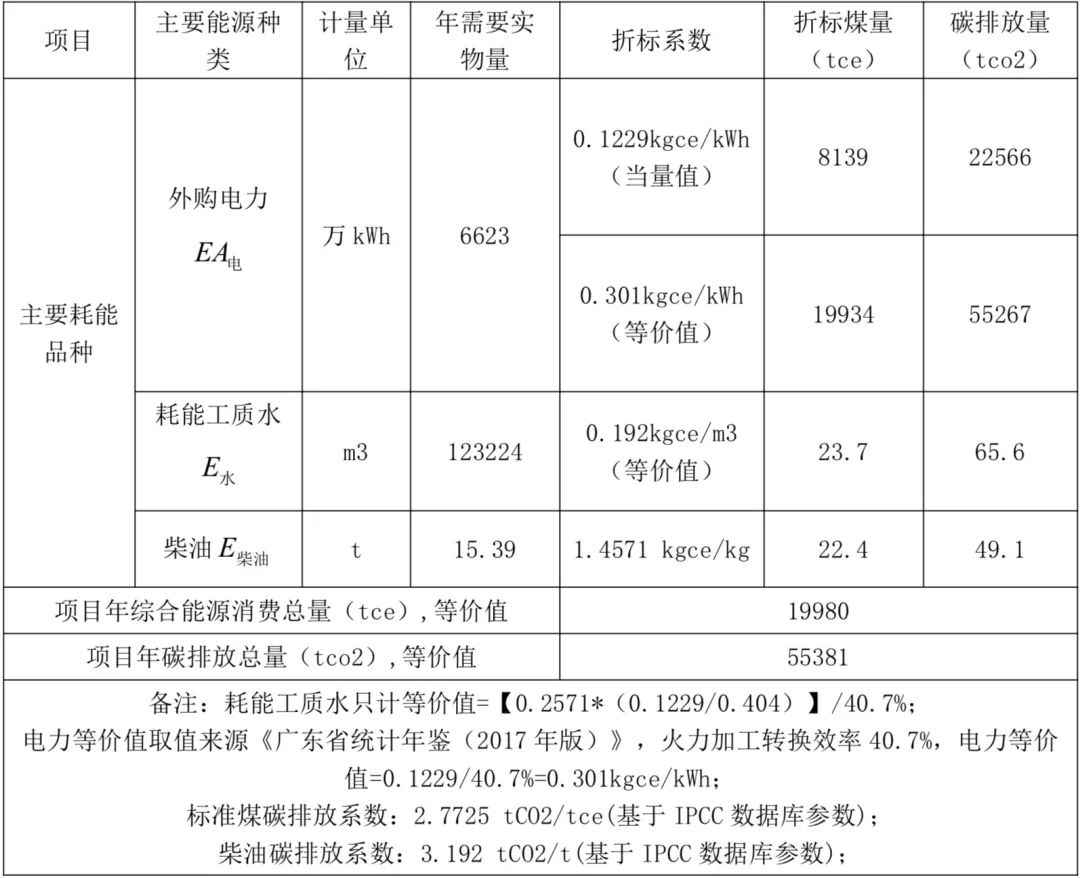
When the project is powered by purchased electricity, it is calculated to consume 19,980 tons of standard coal and emit 55,381 tons of carbon dioxide per year.
3.2 Accounting for the use of natural gas power generation scheme
If the project switches to a gas triple power supply unit, burns natural gas to generate electricity, and uses the waste heat to pass through the lithium bromide unit as the data center for cooling, according to the mainstream gas generator products in the market, every 1m3 of natural gas can generate 4kWh of electricity, and at the same time recover 4kW of cooling capacity, due to the use of lithium bromide refrigeration unit instead of electric refrigeration unit, the conservative estimate of PUE is reduced from 1.35 to 1.30, then the comprehensive energy consumption and carbon emissions of the project are calculated as follows:
Table 5 Calculation of comprehensive energy consumption and carbon emission accounting of projects (natural gas power generation)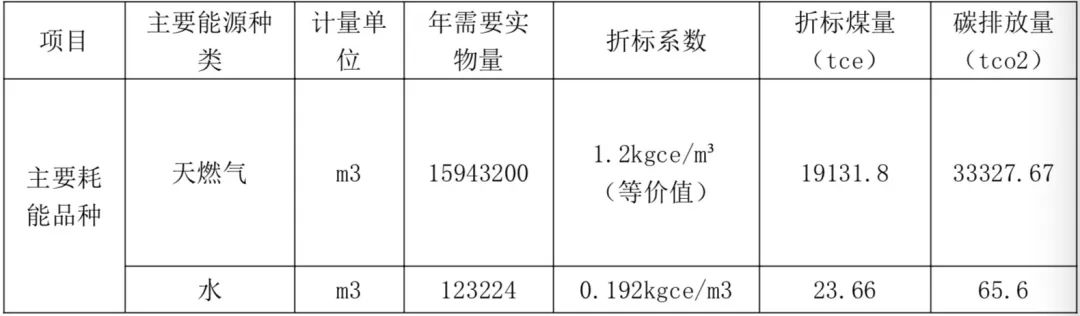
When the project uses natural gas units to generate electricity and lithium bromide units for cooling, it is calculated that it will consume 19,178 tons of standard coal and emit 33,442 tons of carbon dioxide per year.
3.3 Comparative analysis of the two schemes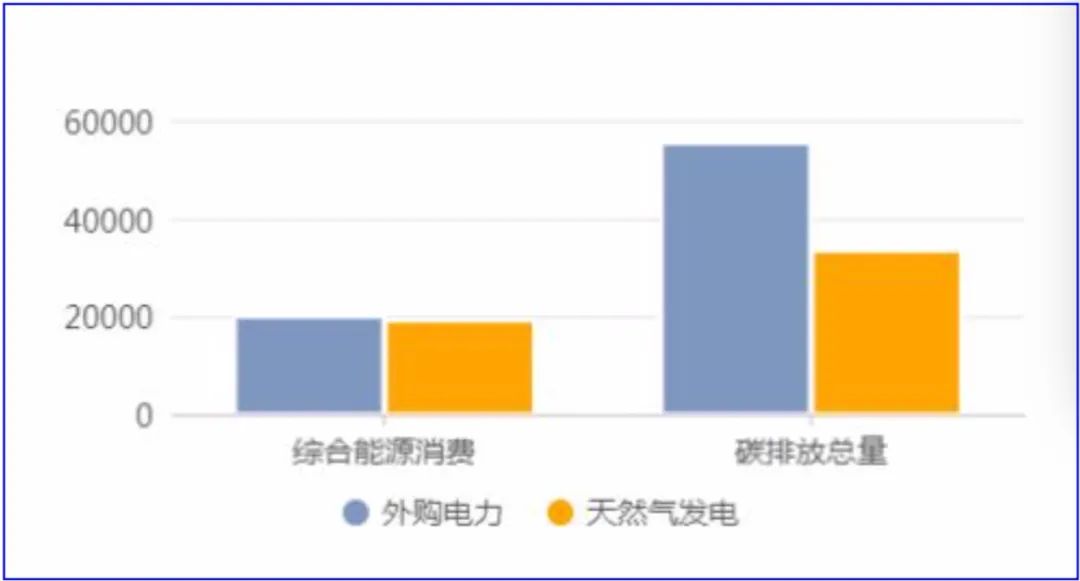
Fig. 1 Comparative analysis of the two schemes
According to the calculation, the comprehensive energy consumption of the two schemes is basically the same; In terms of carbon emissions, the natural gas power generation solution is about 40% lower than the purchased power solution, which shows that the natural gas power generation solution is more conducive to reducing carbon dioxide emissions in data centers.
4 Summary and outlook
As shown in the calculation results, the annual energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions of data centers are very large. According to the calculation of the article, the use of natural gas units to generate electricity and use waste heat to cool the data center through lithium bromide units can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by about 40% per year compared with the traditional method of purchasing mains electricity, which has great potential, but it is still necessary to consider the continuous supply of natural gas, natural gas storage and other issues in the scheme design stage.
As a large energy user, we must actively respond to the national call and continue to explore and practice in data center planning, design, operation and maintenance management, and help achieve the goals of "carbon peaking" and "carbon neutrality".

