When we enter the high-voltage distribution room of the data center, we will find several (usually two or three) DC screen cabinets, one with batteries, one with small switch buttons, and the other cabinet with many alarm signs (lights). It can send alarm signals to the operation duty personnel in time, or directly issue trip orders to the controlled circuit breaker to stop the development of these events. The complete set of equipment that implements this automation measure is generally called a relay protection device. So what does relay protection do?
We have initially established a "static" model of the system in our minds through the introduction of each part of the data center power supply and distribution system, and in the actual production and operation, the relationship between each subsystem changes with time and time. In order to safely and effectively manage such a huge power system, the concept of relay protection and secondary system arises. In this issue, we will introduce the basic principles, basic requirements, basic tasks, classifications and common relay protection in data centers of relay protection.
What is a relay protection device?
●The power system is a real-time and complex joint system composed of power generation, transmission, distribution and consumption. Electrical energy cannot be stored in large quantities, and generation and consumption are almost always balanced, so reliability is extremely demanding – it cannot be interrupted.
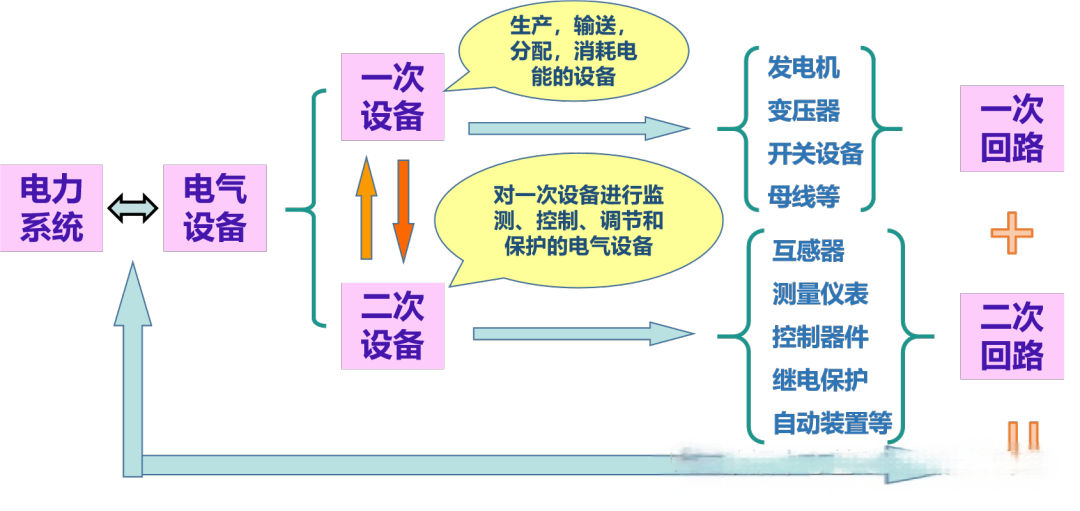
●The power system is divided into: primary equipment and secondary equipment.
◎Primary equipment: electric energy transmission equipment (high-voltage equipment) composed of generators, transformers, busbars, transmission lines, motors, reactors, capacitors, etc.
◎Secondary equipment: equipment that monitors, measures, controls and protects the operating status of primary equipment.
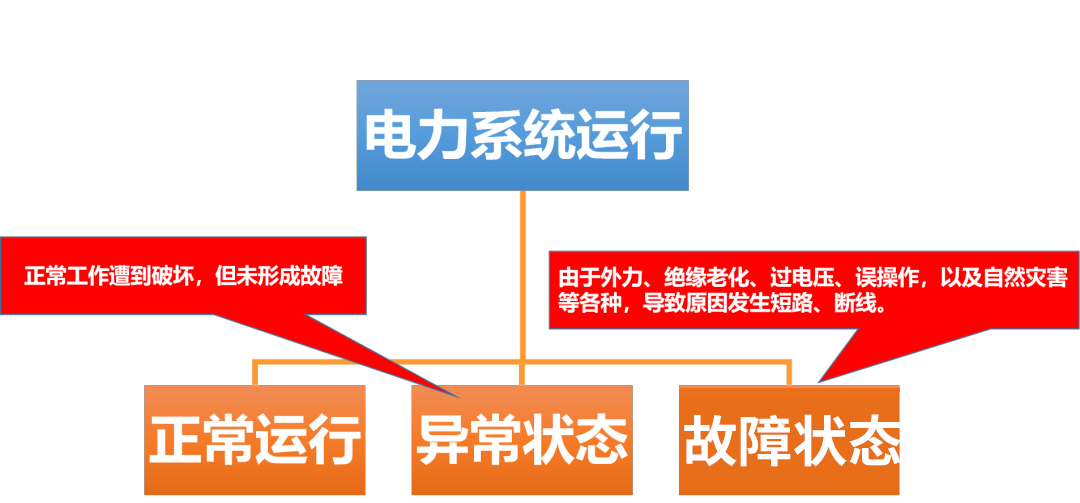
● According to different operating conditions, the power system can be divided into:
◎Normal state: The power system can operate safely and stably for a long time within the specified limits.
◎Abnormal state: Normal operating conditions are disrupted, but no failure has occurred.
◎Fault state: Short circuit and disconnection occur due to external forces, insulation aging, overvoltage, misoperation, and natural disasters during the operation of primary equipment.
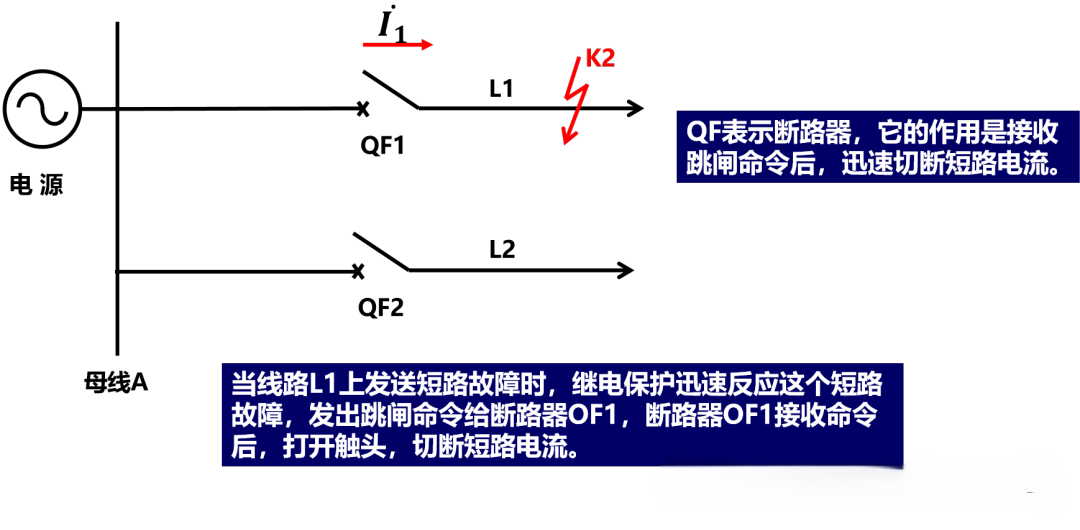
● Automatically, quickly and selectively remove faulty components from the power system, so that other non-faulty parts can quickly return to normal operation.
●Correctly respond to the abnormal operation status of electrical equipment, and issue alarm signals, load reduction or delay tripping according to requirements.

●Rapid mobility: The action time is as short as possible
◎ Fault removal time = protection device operation time + circuit breaker operation time
◎The action time of the protection device is:
◇ The fastest computer protection: 0.01 ~ 0.04 seconds, that is, 0.5 ~ 2 cycles to act
◇Electromagnetic protection: 0.06 ~ 0.12 seconds, that is, 3 ~ 6 cycles of action
◎ Circuit breaker action time:
◇Fastest: 0.02 ~ 0.06 seconds, that is, 1 ~ 3 cycles to break the current
◇General: 0.06 ~ 0.15 seconds, that is, 3~7 cycles of disconnection current
● Sensitivity: There is a specified sensitivity coefficient
● Reliability: The action is reliable, and the action should not be moved
◎ Do not refuse
◎ No mismovement
Note: No power equipment is allowed to operate unprotected.
Composition and principle of relay protection:
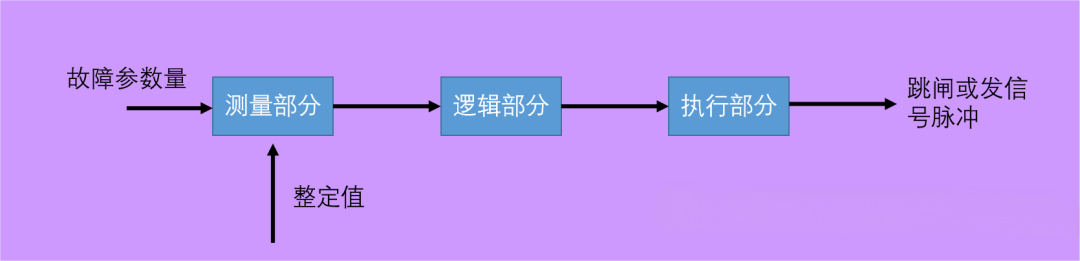
Although there are many principles of relay protection, under normal circumstances, the whole set of relay protection device is composed of three parts: measurement and comparison element, logic judgment element and execution output element.
●Measurement part: (Measuring the working state of the protected object) Measure the amount of electricity concerned, compare it with the set value, and give a set of logic signals with the properties of "yes", "no", "greater than", "not greater", "equal", "0", and "1" to determine whether the protection should be activated.
● Logic part: (judge the working state of the protected object to determine whether the protection device should be activated) According to the size, nature, order of occurrence or logical combination of each output of the measured part, determine whether the circuit breaker should trip or send an alarm signal, and convey the relevant command to the execution part.
●Execution part: According to the judgment made by the logic part, the trip or alarm signal is sent to the control loop or alarm signal loop of the circuit breaker.
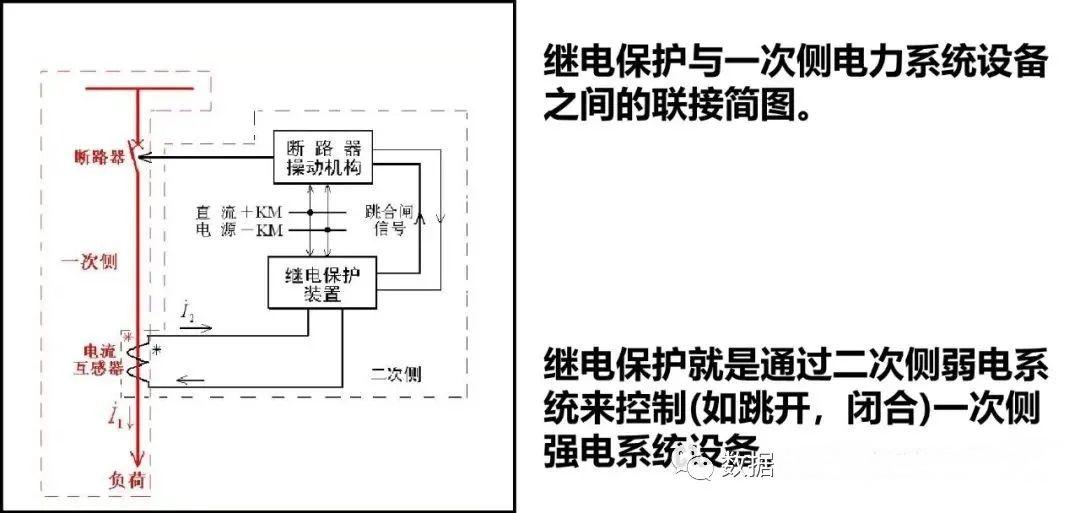
For the operation of medium and high voltage current equipment, the above measurement, logic judgment, execution and other tasks, the relay protection device needs to maintain a certain isolation or coupling relationship with the high voltage equipment. The essence of achieving isolation or coupling is to adopt the principle of electromagnetic mutual induction. The relay protection device is composed of several relays.
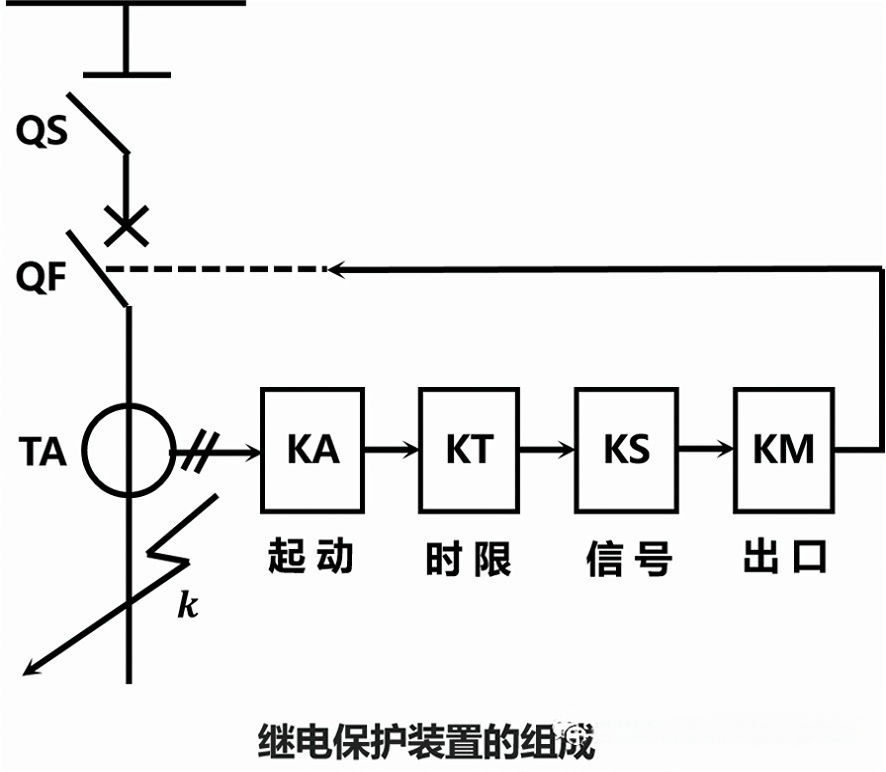
When a short circuit occurs on the line, the instantaneous action of the current relay KA for starting makes the time relay KT start, and after a certain time limit, KT connects the signal relay KS and the intermediate relay KM, and the KM contact connects to the trip circuit of the circuit breaker QF, so that the circuit breaker QF trips.
General power system relay protection types:
The higher the voltage level in the power system, the larger the capacity of the equipment, the more advanced the protection principle, the more complex the protection, and the more types of relay protection devices used.
●According to the amount of electricity being measured, there are four common types of relay protection:
◎ Protection that reflects changes in the number of current values. Including the increase or decrease of various positive and negative currents. There are time-limited overcurrent protection, reverse time-limit overcurrent protection, current speed protection, overload protection, and zero-sequence current protection.
◎ Protection to reflect the change of voltage value. Including the reduction or increase of various positive and negative sequence voltages. There is overvoltage protection and undervoltage protection.
◎ Protection to reflect phase changes between two or more electrical quantities. It includes phase changes between current and voltage, phase changes between current and current, and phase changes between voltage and voltage. For example, directional protection, differential protection, and simultaneous detection.
◎ Protection to reflect the change of impedance of the system. According to electrical principles, impedance reflects the relationship between current and voltage, such as distance protection.
● Frequency protection for reflecting frequency changes in the system.
◎Specially designed for temperature protection to reflect the temperature change of the transformer.
●Classification according to protected objects: transmission line protection, main equipment protection (such as generators, transformers, busbars, capacitors).
●Classification according to protection function: short circuit fault protection, abnormal operation protection.
◎Short circuit fault protection is divided into main protection, backup protection and auxiliary protection.
◎Abnormal operation protection is divided into: overload protection, demagnetization protection, low-frequency protection, non-full-phase protection, etc.
● Classification of signals by protection device for comparison and calculation:
◎Analog operation protection: electromechanical, rectifier, transistor, integrated circuit type (directly reflecting the continuous analog of the input signal)
◎Digital operation protection: The protection device of microprocessor and microcomputer is adopted.
●Classification according to the principle of protection action: over-current protection, low-voltage protection, over-voltage protection, distance protection, differential protection, high-frequency (carrier) protection, etc.
Coordination of relay protection:
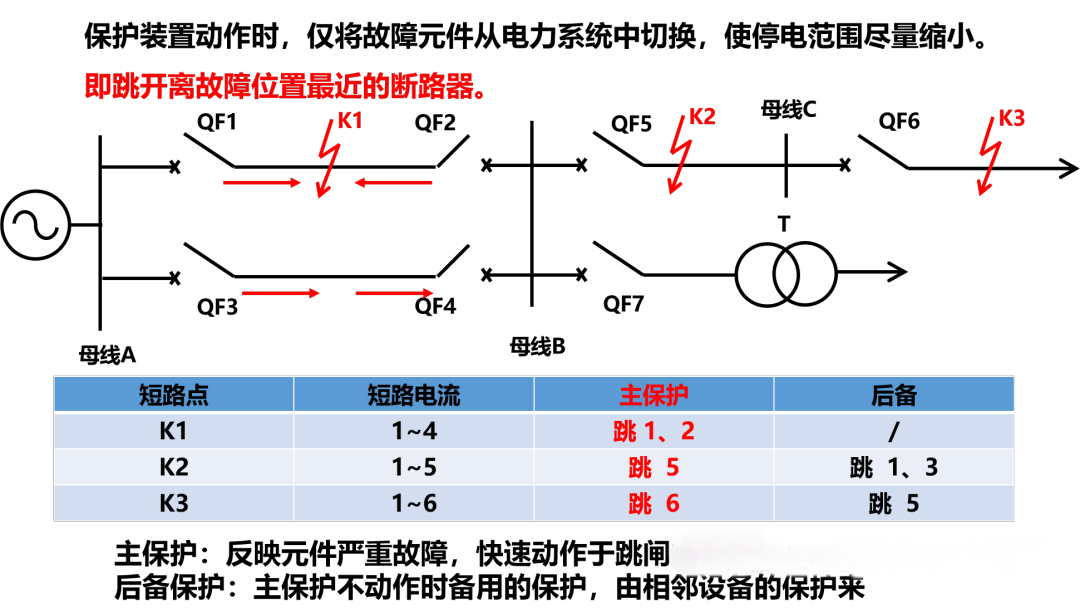
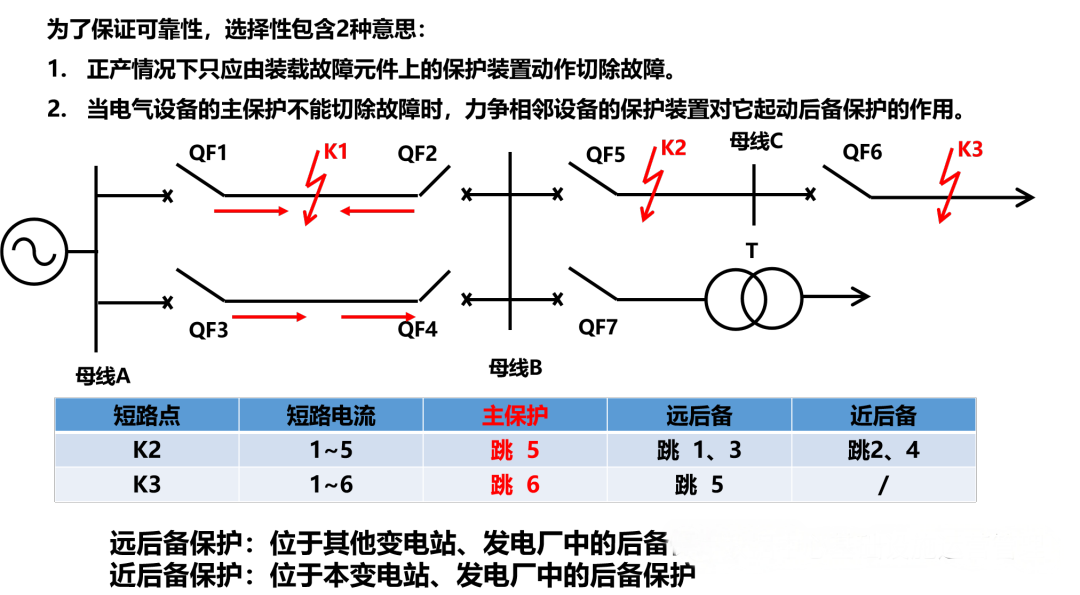
Each set of protection has a pre-defined protection range, which only works if it fails within the protection range. In order to ensure that faulty components can be removed, power equipment and lines in the power system should be equipped with protection devices for short circuit faults and abnormal operation. The protection of power equipment and line short-circuit faults should have primary protection and backup protection, and auxiliary protection can be added if necessary.
●Main protection: meet the requirements of system stability and equipment safety, and can selectively cut off the protection of protected equipment and line faults at the fastest speed.

●Backup protection: When the main protection or circuit breaker refuses, it is used to cut off the fault protection. It is divided into far backup protection and near backup protection methods.

● Auxiliary protection: Simple protection added to supplement the performance of the main and backup protections or when the main and backup protections are out of operation. Such as zero-sequence current protection.
In order to minimize the impact of faults on the power system, it should be ensured that any type of fault should be quickly removed by the main protection, and the general backup protection will be delayed, and the main protection will not be activated before acting. Therefore, there is a cooperation between the main protection and the backup protection in action time and action sensitivity.
Common relay protection in data center distribution systems:
The protection of data center distribution lines should consider preventing personal exposure, electrical line damage and electrical fire in the event of electrical faults. Most of the data center incoming line voltage level is 10kV, while the current 10kV switchgear generally adopts comprehensive relay protection devices, all of which are equipped with relay protection, measurement and display devices.
The commonly used relay protection in data center power distribution systems mainly includes:
●The mains power supply inlet cabinet sets the time limit overcurrent protection, delay current quick break protection, and loss voltage protection.
●The bus cabinet is equipped with current rapid break protection (protection exit after closing) and overcurrent protection.
●The 10kV feeder cabinet adopts quick shutdown protection, time-limited overcurrent protection, temperature protection (high temperature alarm, ultra-high temperature tripping), grounding fault alarm protection, etc.
●The transformer outlet cabinet is equipped with overcurrent protection, current rapid shutdown protection, two-level temperature protection (high temperature alarm, ultra-high temperature trip), grounding fault alarm, and automatic switching function protection for power loss.
●10kV power bus protection and 10kV diesel engine power bus protection adopt bus arc protection, and the protection action time is < 20ms.
●Overload protection, transformer high temperature protection action, trip circuit disconnection, protection device failure, bus loss of pressure, PT fuse fuse, etc.
●Low voltage protection device: the low-voltage main inlet and contact circuit breakers are equipped with overload long delay and short circuit short delay protection trippers, and other low-voltage circuit breakers are equipped with overload long delay, short circuit short delay, and instantaneous tripping according to current capacity; Some circuits are equipped with split excitation trippers, which can cut off the power supply of non-fire equipment related to the fire site in the event of a fire.
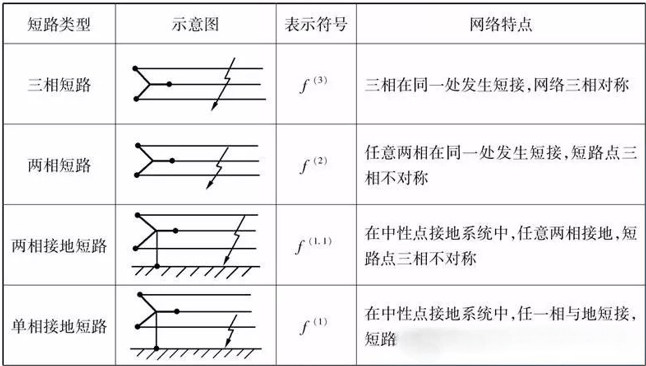
In a 10kV distribution system, a single-phase ground fault, a two-phase short circuit, and a three-phase short circuit fault occur. The main reasons for these failures are the destruction of electrical insulation, such as due to internal overvoltage, direct lightning strike, aging of insulation materials, improper insulation fit, mechanical damage, etc. Certain faults, such as wire breakage and tower collapse accidents, pull-pull disconnect switches with load, circuit breakers with ground wires, etc., may also directly lead to short circuits.
Main faults of the 10kV distribution system:
◎Single-phase grounding
◎ Two-phase short circuit
◎ Three-phase short circuit
Hazards of short circuits:
● Rapid increase in current: the heating of the equipment increases, if the short circuit lasts for a long time, it may overheat or even damage the equipment; Due to the electrodynamic effect of short-circuit current, there will also be a lot of mechanical stress between the conductors, resulting in deformation or even damage to the conductors.
●The voltage drops significantly, which has a great impact on users.
●When the short circuit transmission location is not far from the power supply and the duration is long, the generator running in parallel may lose synchronization, destroy the stability of the system operation, and cause a large-scale power outage, which is the most serious consequence of the short circuit.
●When sending an asymmetric short circuit, the three-phase balanced current will induce an electromotive force on the adjacent communication line, affecting the communication.
Common relay protection for 10kV power distribution system:
●Instantaneous current interruption (time-limited current rapid break): can only protect part of the line, not the entire length of the line.
●Time-limited overcurrent protection (time-limit, reverse-time-limiting): the main protection in the event of a short-circuit fault in the line itself, and as a backup protection for the next level of the line.
◎Time-limiting: The operation time limit of the protection device has nothing to do with the short-circuit current.
◎ Anti-time limit: The short-circuit current is within a small certain range, and the operating time limit of the protection device is inversely proportional to the short-circuit current.
● Zero-sequence grounding overcurrent protection
Protection configuration of 10kV power distribution system: protection device for power supply inlet, distribution line and distribution transformer.
1. Protection configuration of 10kV power supply inlet line
●Timed overcurrent protection (or reverse time-limited overcurrent protection): As a backup protection for bus protection and feeder loop short-circuit faults. In order to meet the requirements of selectivity and reliability of relay protection, three-phase wiring is used for protection;
● Loss of voltage protection: when the 10kV power supply is no voltage, the incoming circuit breaker will automatically trip;
●Zero-sequence overcurrent protection: For the power consumption unit of the substation that uses the small resistance grounding method at the 10kV neutral point, the 10kV inlet circuit breaker should be equipped with zero-sequence overcurrent protection, which acts on tripping after the protection action.
2. Protection configuration of 10kV distribution line
●Current quick break protection (operation time 0s): main protection of the distribution line
◎ Fully star or incomplete star wiring is adopted, and the protection is installed on the power supply side.
◎Scope of protection: Only part of the total length of the line can be protected.
◎Under the maximum operation mode of the power system, it can protect 50% of the total length of the line and has the maximum protection range.
◎ Under the minimum operation mode of the power system, it is not less than 20% of the total length of the protected line, with a minimum protection range.
◎The unprotected part is called the dead zone of quick break.
◎Tuning principle: set according to the maximum short-circuit current that avoids the end of the protected line, that is, the three-phase metallic short-circuit current occurs under the maximum operating mode.
●Time-limited current quick shut-off protection: set to remedy the overcurrent protection action time for too long, or to cooperate with the next level of protection. The main protection of the protected line.
◎ Adopt full star or incomplete star wiring, and the protection is installed on the power supply side.
◎Protection range: It can protect the entire length of the line.
◎Tuning principle: adjust according to the action current that avoids the instantaneous current rapid interruption protection of the next level of adjacent lines.
◎Action time: cooperate with the line current rapid interruption protection.
●Time-limited overcurrent protection: backup protection of the line.
◎ Complete star or incomplete star wiring is used
◎Scope of protection: as the backup protection of the main protection of the protected line, it is called near backup protection; It can protect the entire length of the line; As a backup protection for the next level of adjacent lines or electrical components, it is called far backup protection.
◎Tuning principle: adjust according to the maximum load current that may occur in the line to avoid it.
◎Action time: set according to the principle of stepped time characteristics.
●Anti-time-limited overcurrent protection: the operation time is inversely proportional to the short-circuit current.
●Zero-sequence current protection: The operating current and operation time of zero-sequence current protection are coordinated with the zero-sequence protection of the incoming circuit breaker.
3. Protection device for 10kV distribution transformer
● Current quick break protection: the main protection of the transformer.
◎ Fully star-shaped or incomplete star-shaped wiring is used to protect the installation on the power supply side.
◎Protection range: from the protection installation to the primary high-voltage coil of the transformer, it cannot protect the low-voltage side of the transformer.
◎The low voltage side of the transformer is the dead zone of current rapid interruption protection.
◎Tuning principle: adjust according to the maximum short-circuit current on the low-voltage side of the evasive transformer.
◎Action time: 0s
●Time-limited overcurrent protection: backup protection of the main protection of the transformer, main protection of the low voltage side of the transformer.
◎ It shares a set of current transformers with the current quick-break protection, and the protection is installed on the power supply side.
◎Protection scope: The backup protection of the main protection of the transformer, called near backup protection, can protect the entire transformer; As the backup protection of the main switch on the low voltage side of the transformer, it is called the far backup protection.
◎Tuning principle: set according to the maximum load current of the evasive transformer, including the self-starting current of the motor.
◎Action time: 0.5s
● Current quick break protection: the main protection of the transformer.
◎ Anti-time-limited overcurrent protection: The same effect as time-limit protection, only one of the two is used.
◎Dry-type transformer temperature protection.
◎ Zero-sequence overcurrent protection.
◎100°C fan, 80°C shutdown fan, 130°C over-temperature alarm, 155°C over-temperature trip. Implement according to the manufacturer's instructions.
◎ Threshold protection device for dry-type transformer.
◎When the dry-type transformer has a shell, two doors are provided on the high and low voltage sides, and a limit switch is set on the top beam of each door. Send an alarm signal when the door is opened by mistake.
Introduction to Microcomputer Protection:
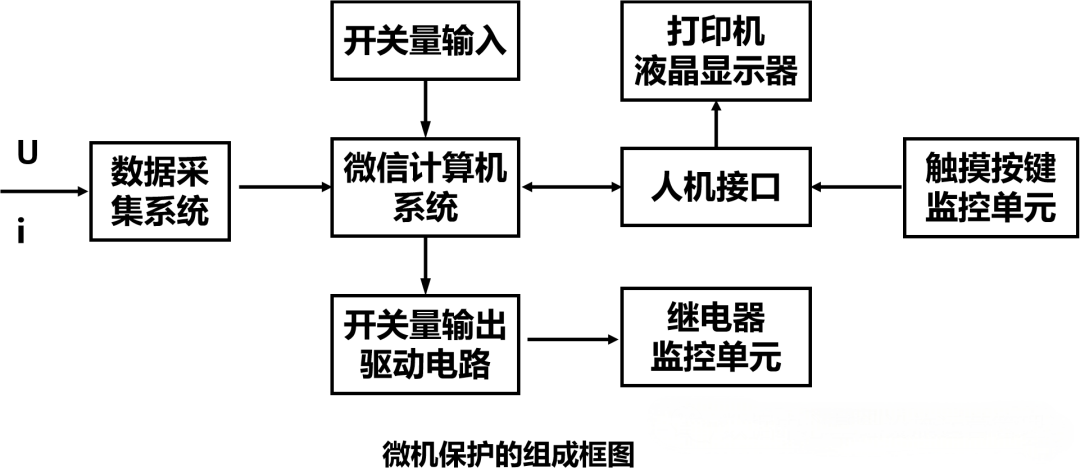
The computer system is used to collect and process the operation data of the power system, quickly and accurately judge the fault and fault range of the power system through numerical calculation, and selectively execute the command such as tripping and alarm after a strict logic process. Since computer systems mostly use microprocessors, they are also called microcomputer relay protection. The hardware composition of the microcomputer protection device can be divided into the following six parts:
● Data acquisition system: accurately convert the analog input into the required digital quantity, which is composed of functional modules such as voltage formation, analog filtering, sampling and holding, multi-channel conversion, analog-to-digital conversion, etc.
● Microcomputer system: It is composed of microprocessor, program memory, data memory, interface chip and timer.
●Input and output interface circuit: input various switching quantities to the microcomputer protection through the optoelectronic coupling circuit and parallel interface circuit, and drive the intermediate relay through the switching output circuit to complete the functions of various protected outlet tripping, signal alarm, etc.
● Communication interface circuit: The communication interface protected by the microcomputer is a necessary condition for the comprehensive automation of the substation, so each protection device has a relatively standard communication interface circuit.
●Man-machine interface circuit: including display, keyboard, various panel switches, printing and alarm, etc., its main functions are used for debugging, setting the value and ratio, etc.
●Power supply: usually uses inverter regulated power supply, that is, DC inverter to AC, and then rectifies AC to DC working voltage required for microcomputer protection.
When we enter the high-voltage distribution room, we will find that there are also relatively independent DC screen cabinets, and the battery placed in one of the cabinets is the operating power supply, mainly to provide the required power to the secondary circuit. For example, if the lighting system of the distribution room fails, the distribution room becomes dark, and we can't work with a flashlight, and this power supply solves the problem of emergency lighting. Of course, its real function is to provide backup power for the relay protection facility, so that when the AC power supply system of the DC screen is blacked out, it can also ensure that the DC screen can also remotely control or operate the opening and closing of the high-voltage circuit breaker and energy storage. At present, large-scale data also puts forward dual thermal backup requirements for DC screen backup battery packs to ensure high reliability of remote control. Therefore, the backup measures for DC screen batteries when building new data centers are also worth paying attention to.

