
1. Basic information of the project:
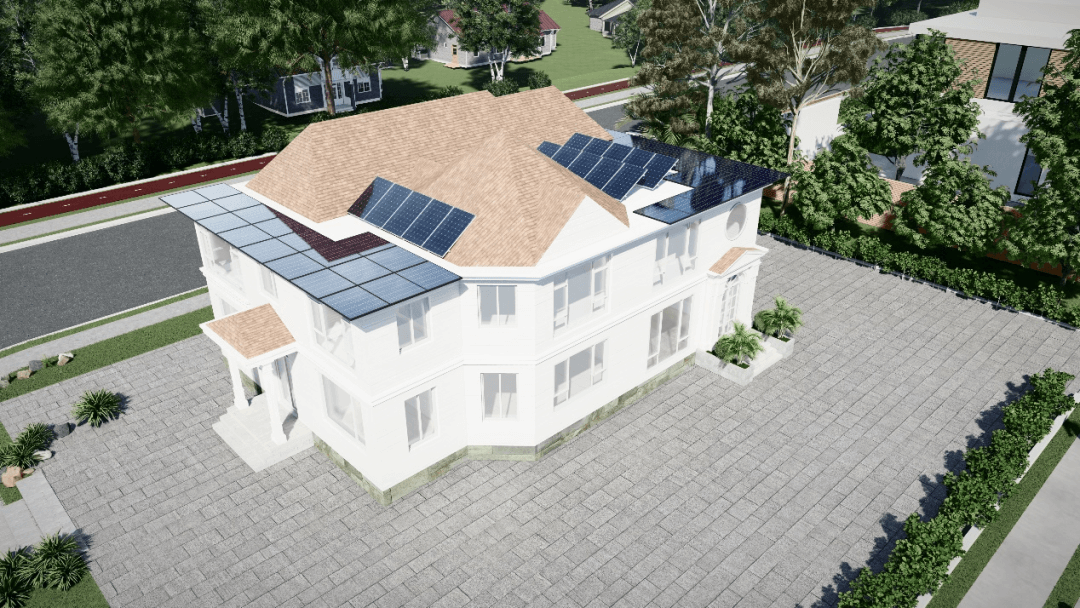
The building is an independent two-storey residential building facing north and south, with a multi-faceted roof and an area of about 500 square meters. It has been built for many years, and the original equipment, facilities and decoration have aged or lost their function, and this time it has been renovated and upgraded as a whole, and it is trying to become a low-energy residential building with the concept of green building and passive house.
Proposed renovation plan, including:
-
The building's envelope has been renovated to introduce some design elements of the passive solar room to improve its natural comfort and energy consumption levels.
-
Heat pump technology is used to provide air conditioning, cooling and heating for the residence;
-
The building will be expanded to the south and north sides respectively to expand the use area, and the extension part is planned to be covered with PVT photovoltaic photovoltaic integrated modules to replace the traditional roof system;
-
Appropriately add PVT modules to the original roof to maximize the installation scale of PVT modules;
-
The photovoltaic power generation system is connected to the grid and operates, and the local consumption and surplus electricity are connected to the Internet to the greatest extent.
-
explore the optimal coupling scheme between PVT and heat pump to further improve the energy efficiency of the entire system;
-
Use heat pump systems to ensure year-round sanitary hot water demand.
2. Give a preliminary plan for needs
2.1 Layout of roof PVT system
The roof of the newly expanded part on the north and south sides of the building is tiled with two sets of PVT modules. The original roof has a south-facing slope, and 4 PVT modules are laid according to the slope. There is a small platform on the original roof, and 4 PVT modules are planned to be installed with brackets. As shown in figure A below, a total of 40 PVT photovoltaic modules with sizes of 2384mm×1303mm and specifications of 660Wp are arranged, with a total installed capacity of about 25.74 KW. It is planned to use one photovoltaic grid-connected inverter (model GW25KF-DT), with a power of 25KW and two 30A inputs.
The roof system of the original residential building is a multi-faceted slope structure covered with dark large corrugated tiles, with a prominent European style and should not be rudely broken. The north and south sides of the outward extension adopt a tiling method to realize the functions of power generation and heat generation, although it is not perfect, but the impact on the view of the whole house is relatively small, and the scheme is within the acceptable range.
the PVT modules installed on the two slopes on the original roofing system are too abrupt and cause too much damage to the appearance of the building; Moreover, the lighting conditions of the four PVT modules located on the small platform are complex, and they are in the same string as the four PVT modules on the south-facing slope in the system, which interferes with each other and affects the efficiency of the system. Therefore, it is necessary to reconsider arranging it on the east-facing and west-facing roofs, as shown in Figure B below, although it also has a certain negative impact on the architectural outlook, but with the increasing public acceptance of rooftop photovoltaic systems in recent years, the neatly laid photovoltaic panels on the roof have become a new label for owners to be avant-garde and advocating environmental protection. The small roof platform is recommended to be restored to a roof garden landscape to enhance the agility of the entire building.
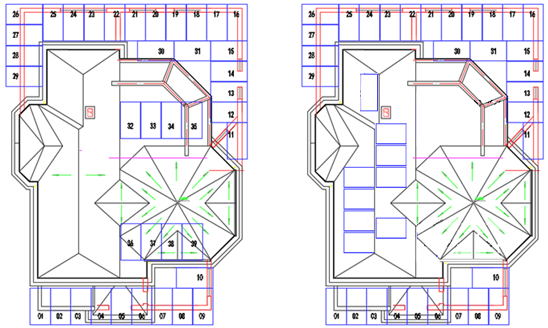
(a) (b)
Arrangement scheme of PVT modules on the roof
2.2 Design of PV system
The original plan plans to use one photovoltaic grid-connected inverter (model GW25KF-DT), which has a power of 25KW and two 30A inputs. Due to the heterogeneity of the roof structure, the PVT modules in different locations have huge differences in the lighting conditions, and the mainstream grid-connected inverters in this power range usually have a small number of MPPT inputs, which is not enough to meet the needs of this complexity, which seriously affects the power generation efficiency of the entire photovoltaic system.
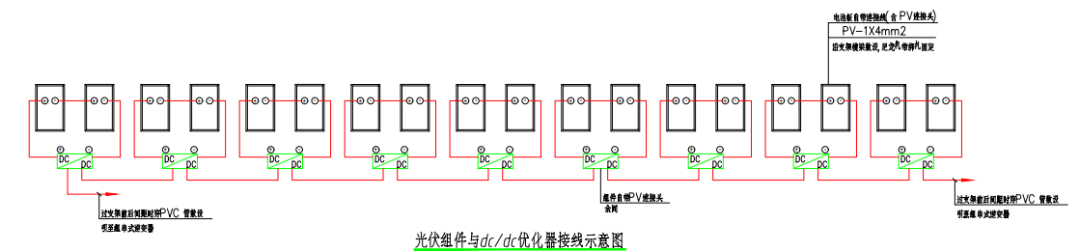
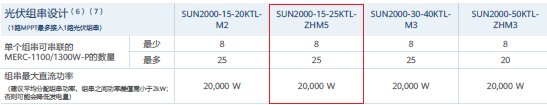
The new solution will use a photovoltaic module optimizer to maximize the power generation efficiency of each panel on the same string, even if the lighting conditions are inconsistent. A total of 40 PVT modules are installed, and the system diagram is as follows:
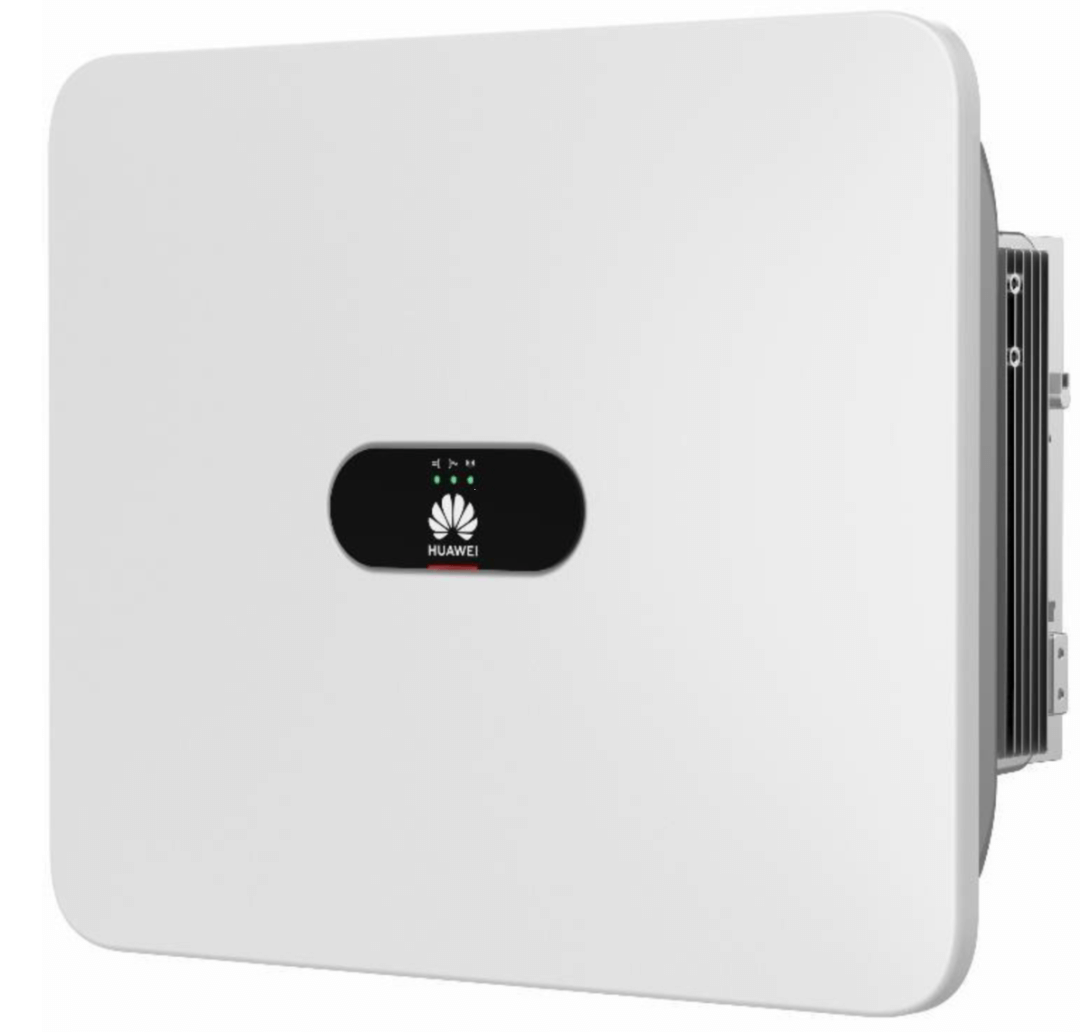
Optimizer selection: Choose the MERC-1300W-P optimizer product produced by Huawei.
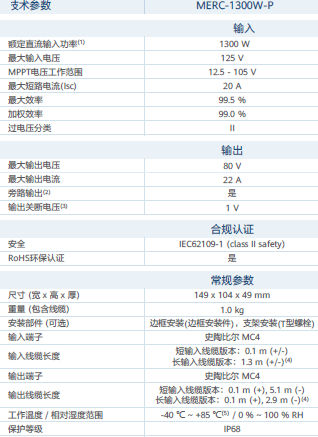
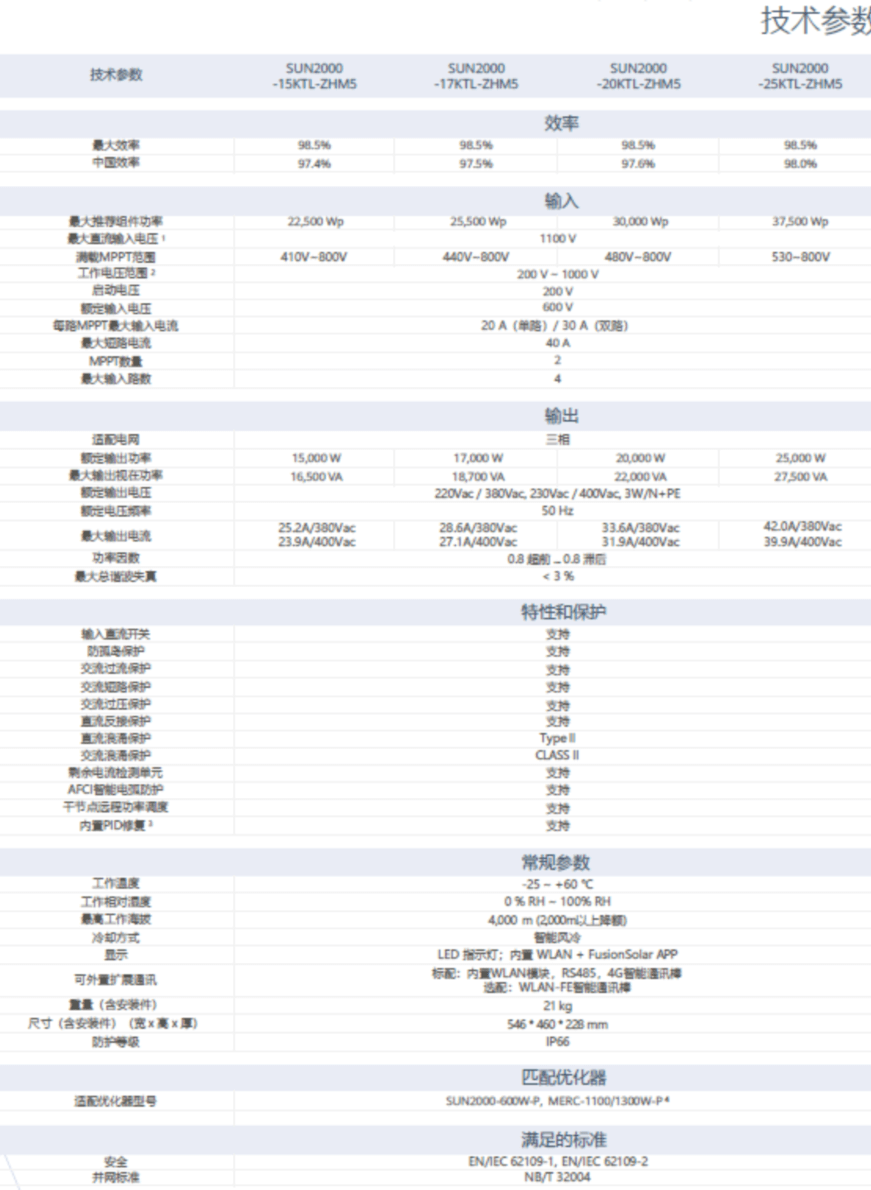
Photovoltaic grid-connected inverter selection: Huawei SUN2000-25KTL is selected.

2.3 Design of heat collection system
PVT modules are products derived from the combination of photovoltaic panels and heat exchanger plates. The "T" in its abbreviation refers to Thermal, which refers to its functional part with heat collection. Usually this part is attached to the part used to collect heat, and it also needs to take into account the normal heat dissipation needs of photovoltaic panels in the event of downtime, so it is not insulated. Therefore, it is only suitable for working under conditions where the difference between the ambient temperature is not large. In practical applications, it is almost necessary to couple it with a heat pump.
In terms of manufacturing process, the most common heat exchanger plates are blown type (a) and tube plate type (b), see the figure below:
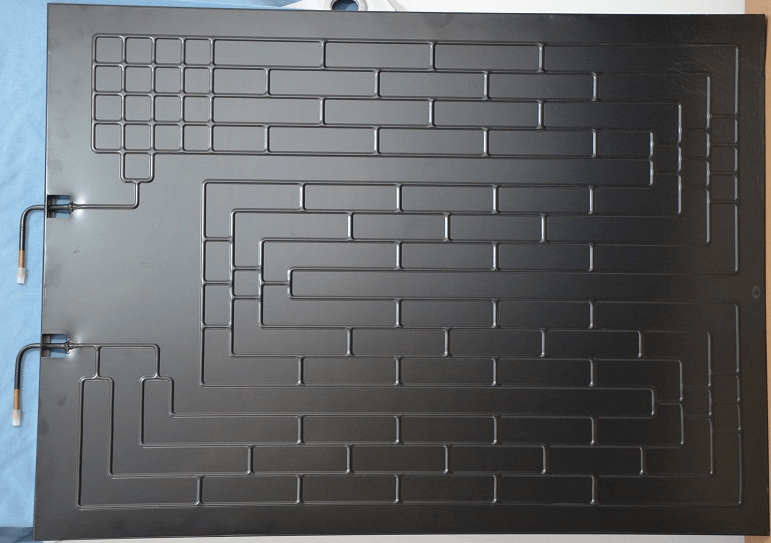

Blowing type (a)
Tube Plate Type (B)
In this project, combined with many factors in system design, comprehensive research and judgment make it more suitable to choose a heat exchanger plate using blowing type. This kind of PVT product, generally the original design uses freon as the heat exchange working fluid, and PVT is used as an evaporator, which has the characteristics of good temperature uniformity, but the price is higher, and due to thermal expansion and contraction, the reliability of the product needs to be carefully screened in combination with the manufacturing process, structural optimization, etc.
In terms of the selection of working fluid, because most of the PVT in this project is tiled, it is difficult to remove the snow once it is covered, and the PVT array is large and the installation situation is complicated, which is not conducive to the return of working fluid and refrigeration oil. Therefore, JM-EC-04 liquid-cooled insulating thermal management fluid was selected as the heat transfer working fluid and applied in the closed circulation system.
The main road of the circulation system adopts welded steel pipe, the specification is DN32, and after leak detection, it is brushed with zinc-rich primer twice and fluoride topcoat twice, and a 20mm thick flame-retardant rubber and plastic insulation system is adopted. All 40 PVT modules are connected in parallel, and branch pipelines are distributed, using 12mm aluminum tubes, and the surface is sprayed with a color coating that blends with the roof, without thermal insulation. The main circulation pipeline is designed according to the shortest pipeline, and 40 manifolds with flow display are used for flow distribution adjustment. The main circulation pump is a fixed-frequency wet rotary lobe pump, with a total flow rate of 2.4m³/h and a head greater than 8 meters, and the specific model is to be determined. The expansion tank uses VR24 airbag type expansion tank.
2.3 Design and selection of heat pump system
The project is a two-story building, with a height of 9.6m and a construction area of 494 square meters, using Haiwu Group's self-produced heat pump as the heating and cooling source for heating and cooling.
Characteristics of annual temperature changes in the project site:
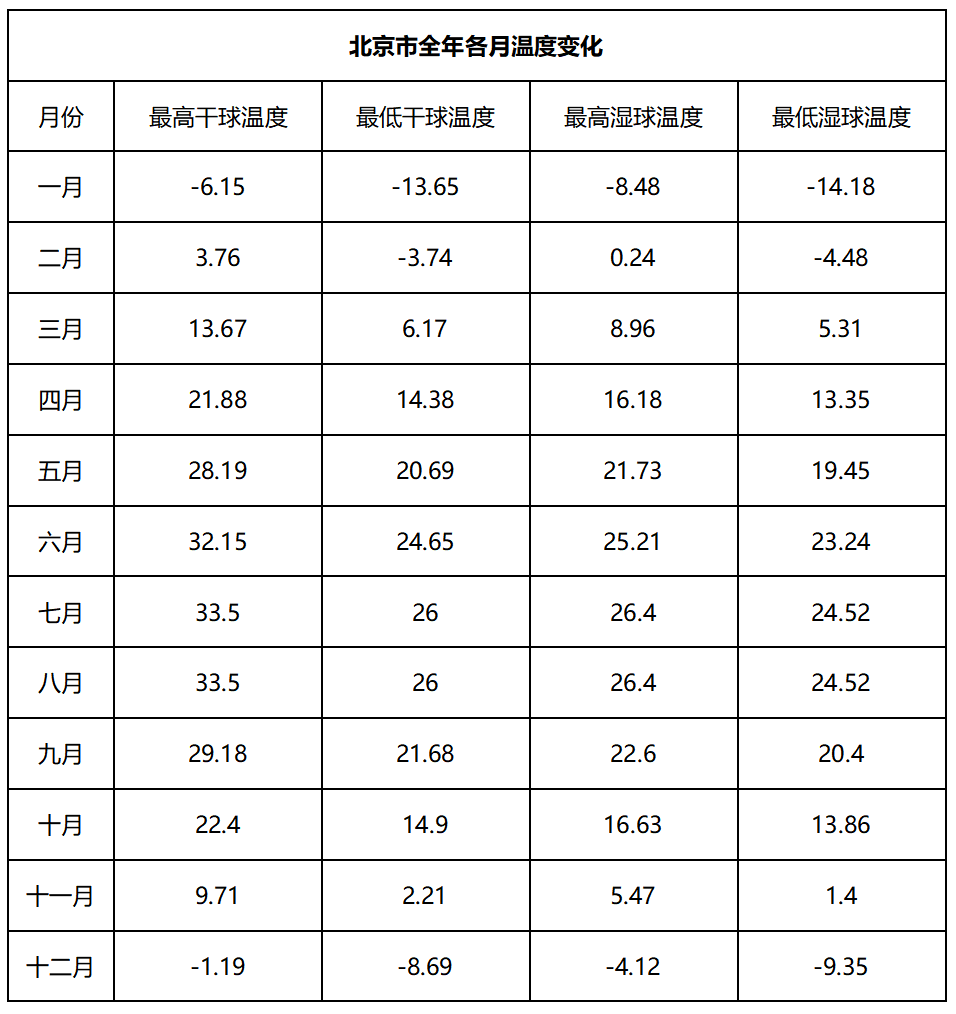
Monthly temperature change curve of the project site throughout the year:
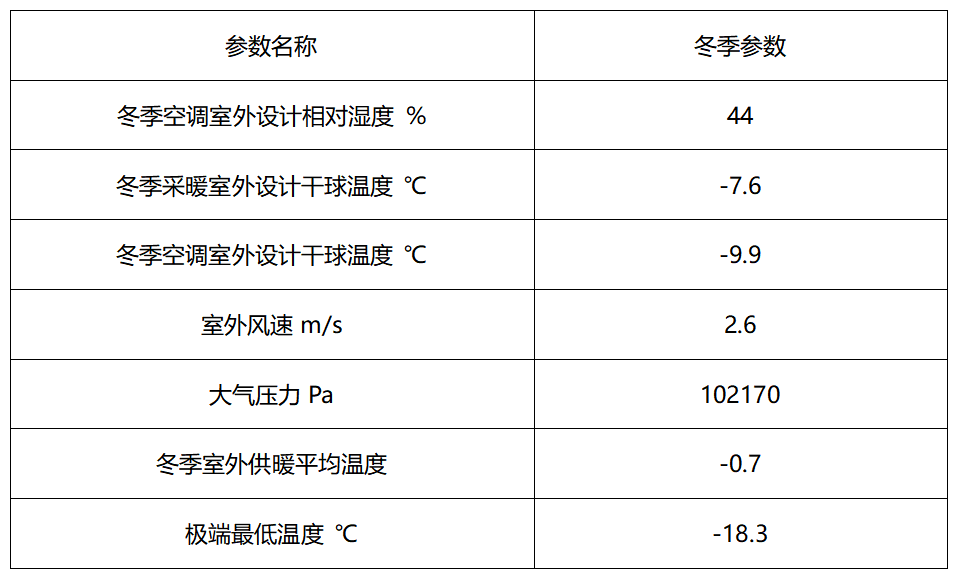
Winter outdoor design parameters:
Summer outdoor design parameters:
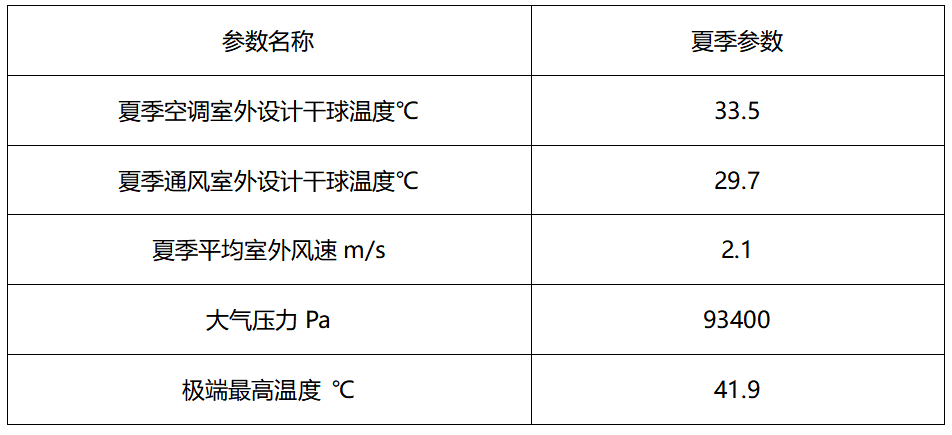
Note: This parameter comes from the design code for heating, ventilation and air conditioning of civil buildings "GB50736-2012"
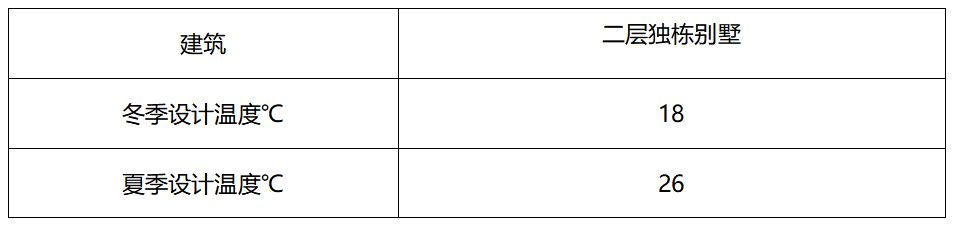
Interior design parameters:
The calculation results of cold and heat loads are shown in the following table:
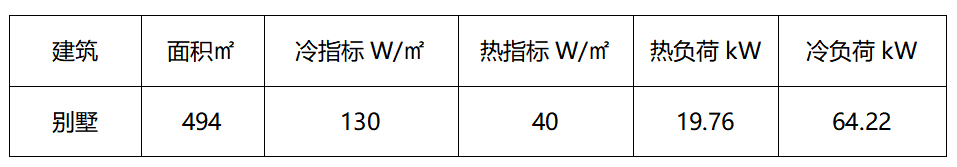
Based on this, it is necessary to analyze and compare the possible system schemes. Obviously, the cooling load of the building is much greater than the heating heat load, and the load of sanitary hot water is negligible compared to the cooling and heating load.
Option 1: Install an air source heat pump that meets the cooling load of 64.22kW. This scheme is a typical three-power system of hot and cold water, and the common system is shown in the figure below. Air source heat pumps are used for air conditioning cooling in summer, heating in winter, heat pump switching heating for hot water in the heating season, and electric heating tubes for heating in the non-heating season. If it is envisaged to use PVT heat to heat the water tank in summer, the complexity of the system should not be too high in view of the small heat demand of hot water, and it should not be adopted. Due to the seasonal contradiction between air source heat pump and PVT heat coupling utilization, this project is not applicable to this scheme.
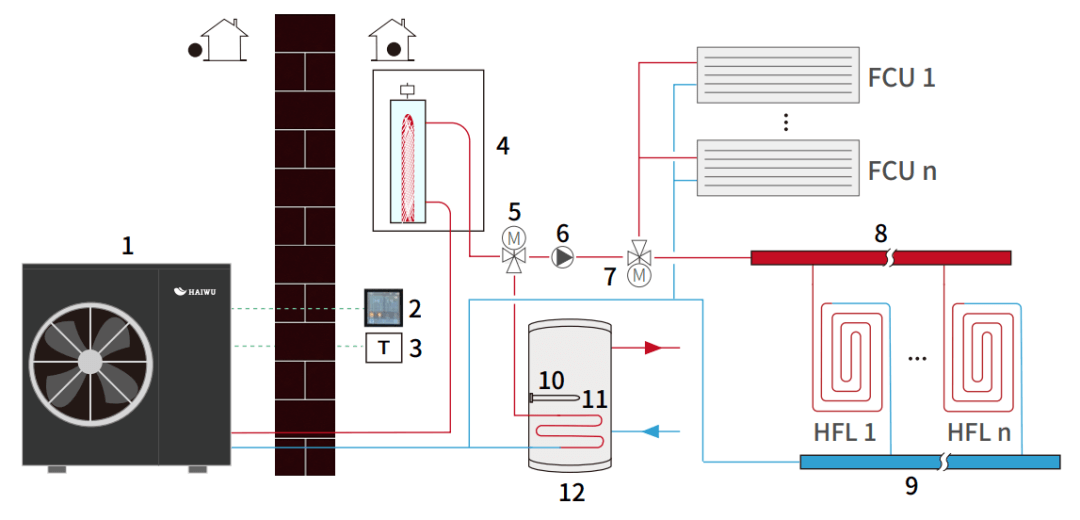
Scheme 2: Install a ground source heat pump that meets the cooling load of 64.22kW, and the PVT is coupled from the heat source end to form a three-unit heating and cooling water supply system, the system is as shown in the figure below. Ground source heat pumps are used for air conditioning and cooling in summer, heating in winter, heat pump switching heating for hot water in the heating season, and electric heating tubes for heating in the non-heating season. In winter, PVT and heat exchange wells provide a higher temperature low-temperature heat source to the ground source heat pump, and the ground source heat pump will obtain a higher operating COP and play a certain energy-saving effect. In summer, the system enters the air conditioning and cooling mode, the heat output of the heat pump is about 80kw, the heat generated by PVT is about 45kW, and the heat needs to be recharged through the ground source well, and about 24 wells are needed to meet the consumption demand, which is obviously impossible from the perspective of site, cost and heat absorption, and the use of additional radiators for heat dissipation is contrary to the significance of using PVT, and this project will not be adopted.
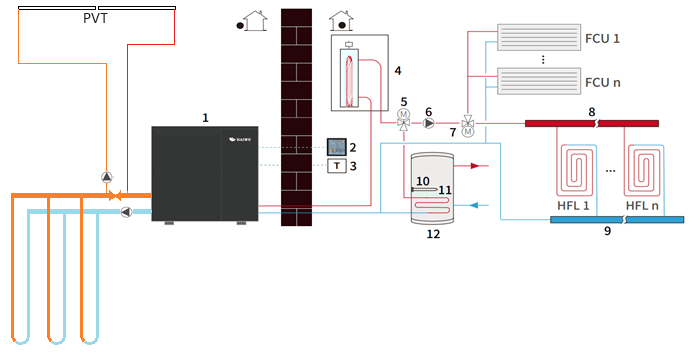
Option 3: Combined with the thinking of Scheme 1 and Option 2, we clarified the direction of demand. In view of the large air conditioning load and strong sunshine in summer, the system should give full play to the advantages of PVT water cooling cooling and efficiency improvement as much as possible, maximize power generation, and recharge heat into the ground source well. Room cooling needs to use the most direct way to dissipate heat to the natural environment as much as possible, and air source heat pumps are undoubtedly the best choice. For winter heating, ground and solar sources can provide efficient and stable low-temperature heat sources, and the use of ground source heat pumps can maximize high-energy efficiency heating, and there will be no frequent frosting of air source heat pumps, which is undoubtedly the best option. In summary, in view of the large difference between heating and cooling loads, the whole system design includes 2 heat pumps: a ground source heat pump with a heating output of more than 19.76kW coupled with PVT for heating, and a single row with a spacing of more than 5 meters to drill 4 ground source wells (double U tube heat exchange) with a depth of 120 meters (double U tube heat exchange) are used outdoors, and the end of the ground pipe is used indoors; In summer, another air source heat pump with a cooling load of 64.22kW is turned on when the air conditioner is used; during the PVT non-heating season, it is heated to the earth through buried wells during the day; and sanitary hot water is provided by the ground source heat pump throughout the year.
Device Location:
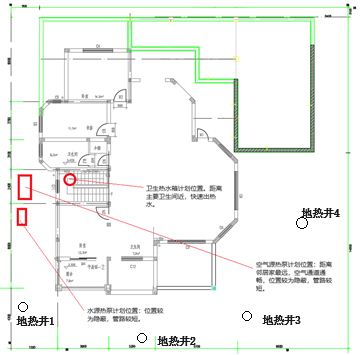
Equipment Selection:
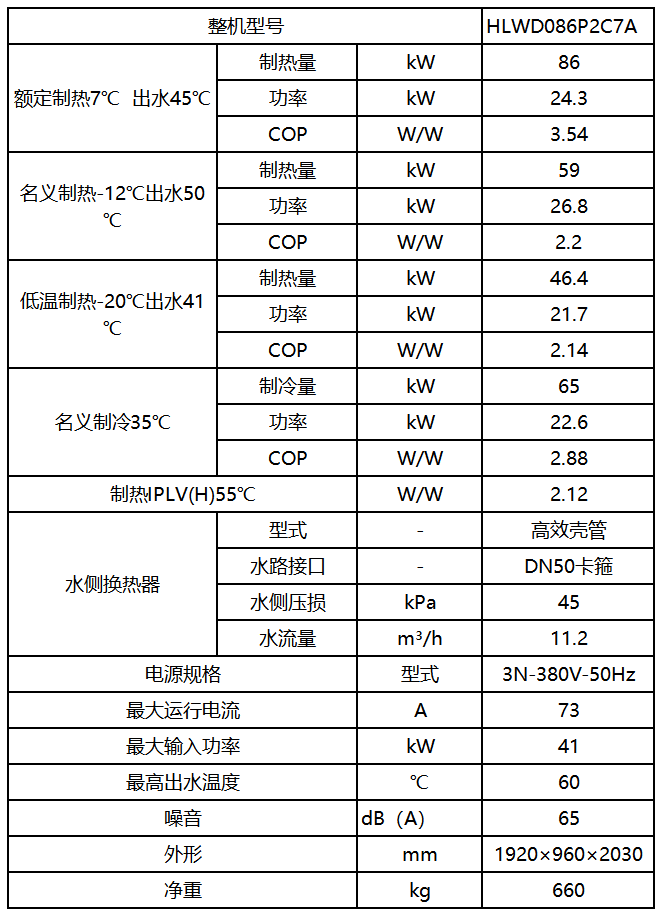
The air source heat pump host is selected with one Haiwu HLWD086P2C7A air source heat pump unit, which has a heating capacity of 59kW and a COP of 2.2 under low temperature working conditions, and can be used as a heating heat source backup in extreme weather or when the ground source heat pump system fails; the rated cooling capacity is 65kW to meet the summer cooling needs of this project.
The specific technical parameters are as follows:
Ground source heat pump host:
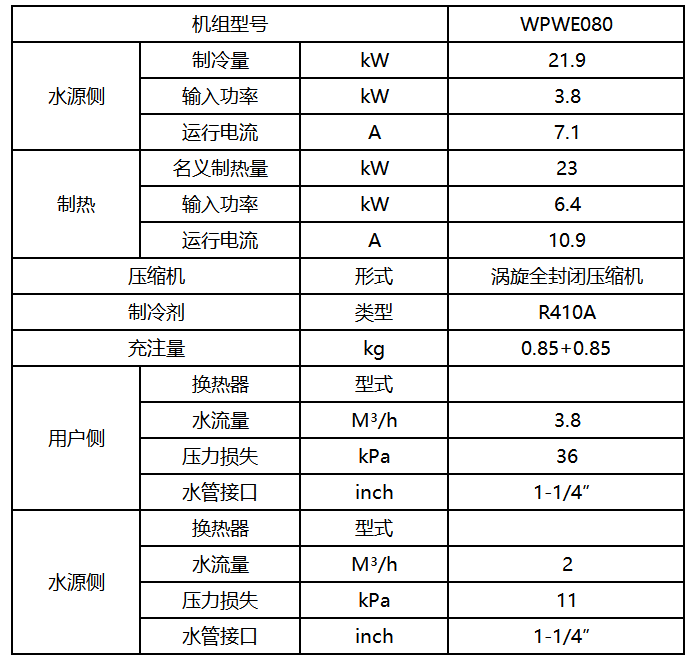
[Note]
1. The unit parameters are tested according to the standard GB/T 19409-2013.

