In today's wave of scientific and technological development, the intelligent computing center stands at the cusp of the times and has become the focus of attention, computing power as the core indicator of the intelligent computing center, determines its ability to process data and perform tasks, and the computing efficiency reflects the utilization efficiency of computing power resources

1. Definition of computing power
Computing power (CP, ComputationaPower) refers to the computing power of a data center.
It refers to the ability of the server in the data center to achieve the output of the result after processing the data, which is a comprehensive indicator to measure the computing power of the data center. The computing power should be the sum of the computing power of all servers in the data center, namely:

2. Classification of computing power
The core elements of computing power (CP) include general computing power (CP-Nomal, abbreviated CPN) and intelligent computing power (i.e., CP-Tuto, abbreviated CPT). General computing power refers to the computing power of a data center server that contains only CPUs. Intelligent computing power refers to the computing power of not only CPUs but also GPUs or AI chips in data center servers. Therefore, the computing power (CP) of the data center:

3. The unit and accuracy of computing power
The most commonly used unit of computing power (CP) is FLOPS (Floatimng point operationsPer Secnd, floating point operations per second). In fact, FLOPS has become synonymous with measuring computing performance in various facilities such as computers, supercomputers, servers, and more. FLOPS is a basic unit, and its larger numerical units are K (thousand), M (trillion), G (gi), T (too), P (beat), E (ai), etc.
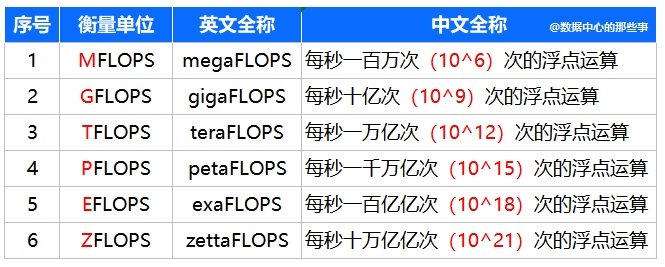
Table 1 Common units of computing power
The accuracy of computing power is different, and the actual computing power level varies greatly. If the computing power level is measured, it is not enough to use the number of operations indicator alone, and the accuracy of computing power should also be considered.
According to the accuracy of the participating computing data, the computing power can be divided into: double-precision computing power (64-bit, FP64), single-precision computing power (32-bit, FP32), half-precision computing power (16-bit, FP16) and integer computing power (INT8, INT4). The higher the number of digits, the higher the accuracy, the higher the complexity of the computation, and the wider the application scenarios.

Table 2 Applicable scenarios of computing power accuracy
However, under normal circumstances, the scale of computing power is uniformly converted into single-precision floating-point (FP32) computing power for statistics.
4. Calculation method of computing power (CP).
From the above, we know that computing power is calculated by adding the computing power of all servers in the data center. If we only know the IT power capacity, how can we estimate the computing power of the data center (intelligent computing center)?
First of all, we should choose an AI server and check its power consumption. Take the H100 GPU server as an example: the CPU consumes about 300W*2, the memory consumes about 250W, the hard disk consumes about 200W, the fan consumes about 150W, and the H100GPU card consumes about 700W*8, and the maximum power consumption is about 6800W. With the H100 module server fully equipped, the power of a single unit is about 10kW. For example, if the total IT capacity of the data center is 8000kW, calculate the number of servers:

From the above formula, it is calculated that 800 H100 GPU servers can be deployed in this data center. The server's GPU hashrate is then calculated.
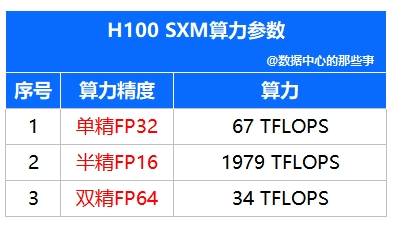
Table 3 Computing power parameters of H100 SXM
According to the above table, the H100 GPU has a single card computing power of 67 TFLOPS, and a single server has a total of 8 GPU cards. Ignoring the CPU computing power, the computing power scale of the data center can be calculated as:

From the above formula, 428,800 TFLOPS (half-precision FP32) can be calculated, that is, 428.8PFLOPS (half-precision FP32). In general, it is recommended to add computing power accuracy at the end to avoid ambiguity.
5. Calculation method of calculation efficiency (CP).
Computational Emciency (CE) refers to the ratio of computing power to power in a data center, that is, "computing power per watt of power in a data center", which is an efficiency that considers both computing performance and power in a data center. The higher the value, the stronger the computing power per unit power and the higher the efficiency. If CP is the computing power of the data center with a single precision floating point number (FP32), and PC is the overall power of the data center IT equipment, its unit is watts (W), then the formula for calculating the effective CE is:

Taking the above data center as an example, substitute the computing power of 428,800 TFLOPS (half-precision FP32) and the total IT capacity of 8000kW to calculate:

The calculated computing efficiency of the data center is 5350FLOPS/W.
In fact, whether it is a data center or an intelligent computing center, it is not difficult to calculate computing power and efficiency, and many construction units have no concept of computing power, so they start construction with the tuyere, which is easy to cause mismatch of resources and insufficient power in the later stage. In order to ensure the safe operation of the data center (intelligent computing center) in the later stage, it is a crucial step to plan the computing power and computing efficiency of the intelligent computing center in advance and study relevant policies.

