Abstract:Liquid cooling technology is an important means to solve the problem of energy conservation and carbon reduction in data centers, especially single-phase immersion liquid cooling technology, which has significant energy-saving effects, and its application is becoming more mature and reliable, and it is gradually favored and chosen by the industry. However, the application and design of liquid cooling technology have certain differences and differences compared with the traditional computer room HVAC design, coupled with the current liquid cooling data center projects are relatively limited, practitioners are relatively unfamiliar with this, combined with the practice of liquid cooling projects, the characteristics of immersion liquid cooling technology and the differences in the design of traditional cooling methods are analyzed, and the key points of design are summarized, especially the design of liquid coolant system. For the newly built and renovated liquid-cooled data centers, different schemes are proposed for the selection of cold sources and the design of cooling water systems, which provide reference and discussion for the subsequent application of liquid cooling technology.
Key words: single-phase immersion liquid cooling; data centers; liquid-cooled cabinets; coolant; CDU; cooling water
Computing power is an important development factor of the digital economy and the core support force for promoting the development of the digital economy. As the main carrier of computing power, data centers are indispensable for their development and large-scale construction. According to the statistics of relevant departments, the annual electricity consumption of our country's data centers in 2021 has accounted for about 1% of the electricity consumption of the whole society, and the use of green energy and energy conservation and carbon reduction have become important goals and topics of data centers, especially for new data centers, national standards and local policies have put forward strict requirements and restrictions on power use efficiency (PUE).
Under the background of the national dual carbon strategy and strict restrictions on PUE in various places, various energy-saving technologies in the field of data centers are blooming, and liquid cooling is gradually favored for its innate energy-saving attributes. Especially in areas where summer is hot and winter is cold, summer is hot and winter is warm, and the energy saving effect of liquid cooling technology is particularly significant. At present, the main liquid cooling technologies used are divided into indirect contact cold plate liquid cooling, phase change liquid cooling, single-phase immersion liquid cooling and single-phase spraying, each with its own advantages and disadvantages [5-6].
1. Immersion liquid cooling is different from traditional cooling systems
Immersion liquid cooling technology mainly uses the two characteristics of a specific liquid, namely liquid efficient heat exchange characteristics and good insulation, to cool the server. The system architecture is relatively simple, the specific cycle flow is shown in Figure 1, the liquid cooling cabinet is used to submerge the server in Figure 2, the coolant distribution unit (CDU) is used to control heat exchange and drive the coolant circulation, and the cooling tower (or dry cooler) is the "cold source" for the entire liquid cooling system to run and dissipate heat.
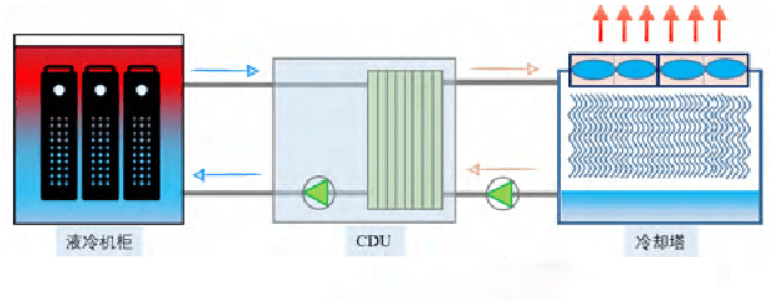

Figure 2 Submerged server liquid cooled cabinet
From the flow chart, immersion liquid cooling no longer needs to rely on compressor cooling, and mainly relies on natural cold sources for heat exchange. Compared with the chilled water (or direct expansion machine) system of traditional air-cooled servers, the main features of immersion liquid cooling are as follows:
1) The coupling degree between the liquid-cooled cabinet and the cooling circulation system is very high, and the design needs to pay more attention to the circulation system composed of the liquid-cooled cabinet and CDU;
2) The server in the immersion liquid-cooled cabinet has changed from the traditional horizontal plugging to vertical up and down installation, and the change of plugging and unplugging method has led to a decrease in the cabinet rate of the flat layout, and the design needs to pay more attention to the layout of the liquid-cooled cabinet to improve the cabinet rate.
3) The cost of coolant is high, and it is necessary to pay attention to how to reduce the amount of coolant in the system design process.
4) The cabinet is full of coolant, and different coolant densities are different, so the load-bearing of the floor needs to be paid attention to during the design process. The following are two different layout schemes designed by a project A and a project B based on the above principles. The system architecture is 2 CDUs (1 for 1 standby) connected to 6 liquid cooling cabinets to form a set of coolant circulation system, and then connected to all CDUs through cooling water pipelines to form the entire cooling water system, all pipelines are arranged under the overhead floor, see Figure 3~Figure 6.
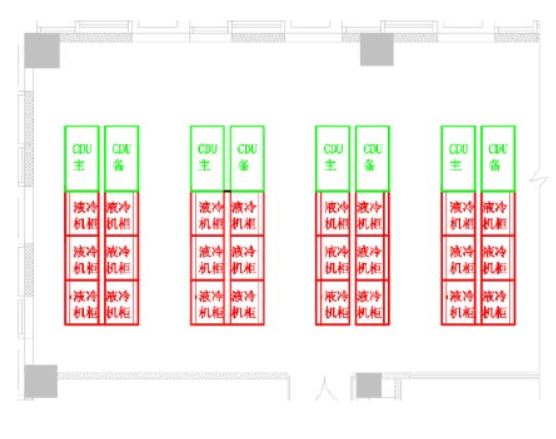
Fig.3 Layout scheme of liquid-cooled cabinet for item A (back-to-back)
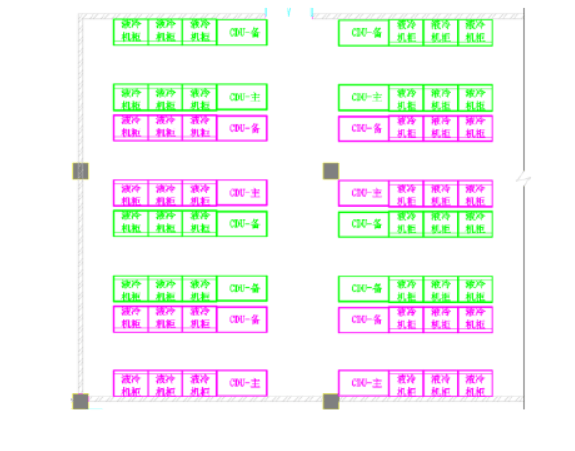
Fig.4 Layout scheme of the liquid-cooled cabinet of Project B (face-to-face)
Both schemes are designed based on the principles of the above analysis:
1) Arrange the liquid-cooled cabinets back-to-back or face-to-face on a large scale, and then connect as many liquid-cooled cabinets as possible through CDU, similar to the multi-connection one-to-many method, to improve the out-of-the-box rate.
2) Arrange the liquid cooling cabinet and CDU nearby to shorten the distance of coolant circulation and reduce the amount of coolant used in the pipeline system;
3) The CDU is centrally arranged in one area or several orderly areas, so that the liquid cooling equipment pipeline and cooling water pipeline have a clear physical partition, on the one hand, the orderly layout of each functional area, and on the other hand, the redundant design of cooling water pipeline and valve can be more concise.
The two schemes are similar but different, with the most obvious difference being the difference in the coolant lines. In order to achieve the continuity of coolant circulation and avoid single point failure, according to the respective building conditions, the coolant pipeline of Project A adopts the method of double supply and double return, and Project B adopts the method of ring pipeline, both of which can achieve system redundancy, see Fig. 5 and Fig. 6. Through comparative analysis, the functions and reliability of the two methods are the same, and the system pipelines have their own characteristics, and the actual application process can be selected in combination with different building layouts, size areas, cabinet rates, and operation and maintenance channels.
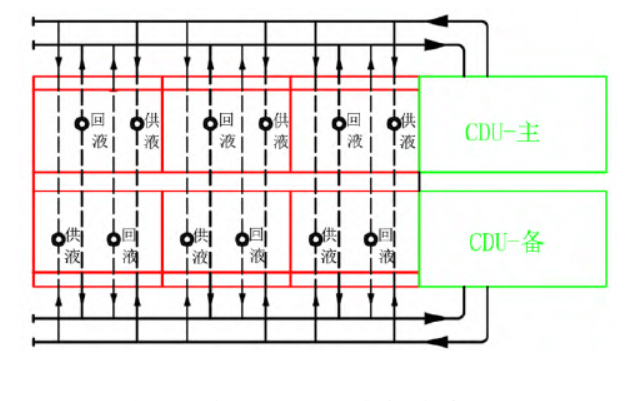
Fig.5 Coolant pipeline layout of Project A
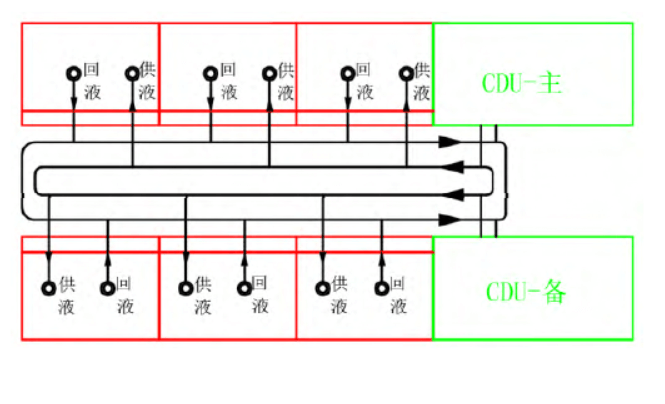
Fig.6 Coolant pipeline layout of project B
2. Selection of cooling source for new immersion liquid-cooled data center
In a new immersion liquid-cooled data center, the choice of cooling source is crucial in addition to liquid-cooled cabinets and CDUs. Due to the efficient heat transfer characteristics of liquids, the coolant is allowed to operate at temperatures much higher than that of air-cooled environments, while still maintaining a good CPU core temperature. According to the specifications issued by the Chinese Institute of Electronics, the liquid supply temperature can operate in the range of 25°C~50°C [7], in such a wide and high temperature range, there can be a variety of heat exchange and cooling source options, usually more economical and reliable are dry coolers and cooling towers, if there is available wastewater waste cooling around, it is also a good choice. For small-scale liquid cooling, the cold source is often mainly a dry cooler, and the coolant is exchanged through the dry cooler and outdoor air, and the system has few components and is simple to control. For computer rooms with a slightly larger volume, the cooling source is mainly the cooling tower. Choosing between an open cooling tower or a closed cooling tower for a cooling tower is also the most difficult choice in actual projects.
The author combines the actual operation of the two cooling towers to compare and analyze the advantages and disadvantages of the two. The closed cooling tower is its biggest advantage because the cooling water is not in direct contact with the external environment, and the water quality is easy to control, which is also the preferred choice of many designers. However, in the process of actual project landing, it was found that the closed cooling tower is large in size, covers a large area, and the price is higher, and the price of the closed tower is 3 times ~ 5 times higher than that of the open tower under the same design conditions. In particular, the data center industry pays more attention to equipment brands, making closed cooling towers account for a large proportion of investment costs. Secondly, for the cold areas of the north, if a closed cooling tower is used, ethylene glycol also needs to be added to the pipeline, which is an organic matter and is easy to breed bacteria and microorganisms. After long-term operation, the aqueous ethylene glycol solution is easily oxidized if not well controlled, forming carboxylic acids, etc., corroding pipelines and heat exchange coils [8-9], Fig. 7 shows the water quality of a project after the operation of closed tower with ethylene glycol, which has obvious corrosion. In addition, the closed cooling tower uses water spray for heat exchange, and an additional power consuming equipment spray pump is added; At the same time, for the cooling water with ethylene glycol, due to the low specific heat capacity of ethylene glycol is 2.35kJ/kg·°C, which is only about half of the water, resulting in a decrease in the circulating heat transfer efficiency of the system, and the operating power consumption of the system increases by about 10%~20% according to different ethylene glycol addition ratios. If you can weigh the advantages and disadvantages as above, a closed tower will be a good choice for a system.

Open towers are more commonly used in conventional chilled water systems, and one of the advantages is that they are less expensive. Secondly, the open tower system is simple, does not require a fixed pressure device of the closed system, there is no spray pump, no need to add ethylene glycol to prevent freezing, and the operation and maintenance are simple. And under the same working conditions, the equipment power is low, and you can even choose some fanless cooling towers to operate, which can reduce PUE to the extreme. However, the biggest disadvantage of the open tower is that the circulating water is in direct contact with the external environment, and it is necessary to focus on water quality treatment. The author is fortunate to participate in the project with good water quality control of the open tower system, see Figure 8 The water quality is clear and good. The specific measures are to use galvanized pipe flange connection, instead of using carbon steel pipe to brush the outer surface of the pipe with anti-rust paint, using galvanized pipeline system, daily operation only needs to deal with the problem of scaling and summer algae bacteria breeding, and the cost of water treatment is greatly reduced. And the cost increase caused by the use of galvanized pipelines is less than 10% of the cost of pipelines, which can be fully covered by the cost reduction of water treatment. By taking the above measures, you can not only save costs, but also control water quality and reduce the use of water treatment chemicals.

The author analyzes and compares the advantages and disadvantages of the two types of towers in actual use and countermeasures from different aspects, and can be combined with the above analysis to make targeted choices in actual projects. In terms of the author's personal point of view, it is recommended to choose an open cooling tower, at present, immersion liquid cooling has not been used on a large scale, the cost of liquid cooling equipment and coolant is relatively high, the use of open cooling tower can appropriately reduce the cost index per kW of server power, and by taking appropriate measures can control the water quality well, in meeting the premise of function, the low-cost solution will be a better choice.
3. The choice of transforming the existing machine room into a cooling source in the submerged liquid-cooled computer room
In order to promote the dual carbon goal, Shanghai and Shenzhen have successively issued implementation plans, especially for the old stock data center computer rooms, the energy consumption is not up to standard, the energy consumption is restricted, eliminated, and upgraded [10-11], this part of the computer room itself is relatively high, if some modifications are made on the existing system, the PUE decrease is not obvious, but the transformation from air cooling to liquid cooling will be a way to achieve significant results. The difficulty of liquid cooling in the transformation of existing machine rooms lies in the redundant design of cold sources. The author provides the following plan for reference based on past project practice.
Option 1): The new cooling water system is independent of the existing system, which is basically similar to the design of the new computer room, but most projects usually do not have good conditions, and different projects will have different constraints.
Option 2: Design using old existing cooling water and chilled water as the primary and backup of the liquid cooling source. Usually, most of the renovation projects are to demolish the existing air-cooled computer room, and use this part of the power and physical space to transform it into a liquid-cooled computer room, so that the system can use excess cooling water as the main cooling source of liquid cooling. At the same time, there is a surplus chilled water pipeline at the end of the original dismantled air conditioner that can be used nearby, so that there is a backup cold source, although the high-grade low-temperature chilled water generated by the compressor is used, but for the liquid cooling system as an emergency backup, it will not cause a significant increase in energy consumption, see Figure 9 for details.
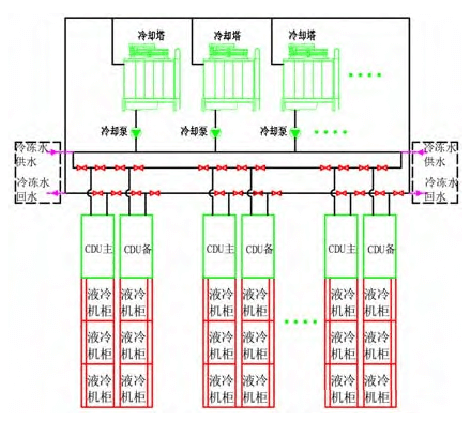
In the process of system transformation, special attention needs to be paid to the following aspects. First, the water quality operation of the original cooling water system, if the water quality is poor, in order to avoid contaminating the chilled water system when switching to chilled water as a cold source operation, a filter can be added to the chilled water return pipeline for treatment and then returned to the overall chilled water pipe network system. Second, in the process of switching, it is necessary to calculate the pressure of the liquid-cooled CDU in the cooling water system and the chilled water system when the pipe network is running, the two are close to the optimum, if the pressure of the chilled water operation is higher than the pressure of the cooling water operation, the switching process focuses on the time of valve switching, and at the same time, it is necessary to monitor the water replenishment of the chilled water system itself in normal operating conditions to avoid the rapid drop of chilled water pressure and affect its own operation. The third is the valve setting on the cooling water pipeline, to avoid over-designed over-allocated valves, and avoid the valve design method of directly using traditional chilled water system pipelines without analysis. According to the GB50174-2017 Data Center Design Code, end equipment such as chilled water precision air conditioners are usually designed according to N+1, that is, there is one backup; In order to realize the maintenance and replacement of valves in the event of a single point failure during operation, usually the end equipment will be designed with two valves in succession, see Fig. 10 [12], when one of the valves fails, the left and right adjacent valves of the faulty valve can be closed, and only one equipment needs to be stopped, without affecting the normal use of the number of main equipment. However, for liquid cooling systems, usually CDU is 1 for 1 standby, and the adjacent group is also 1 for 1 standby, and the valves between the two groups of CDUs can have the original 2 valves and only 1 valve is retained; When one of the valves fails, the partition function can be achieved by closing the A1 and A2 valves, as shown in Figure 11. Although it is necessary to shut down two CDUs, having one backup for each of the two sets of equipment will not affect the normal use of the equipment.
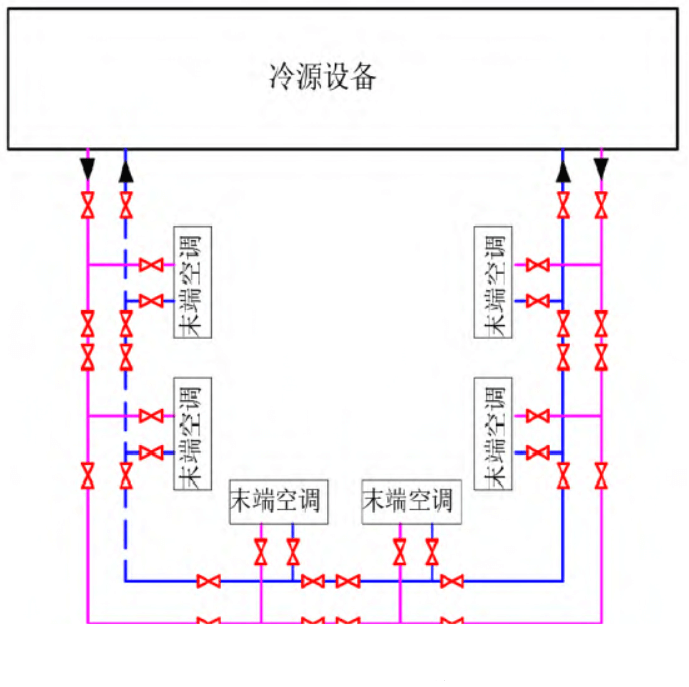
Fig.10 Design of the terminal valve of the chilled water precision air conditioner
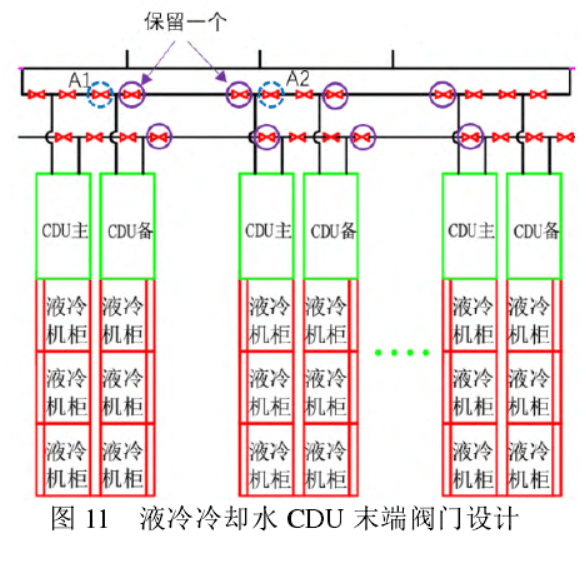
Through the above analysis, for the existing data center, the use of existing cooling water and chilled water as shown in the above scheme 2) not only saves the investment in new cooling equipment and pipeline valves, but also realizes the redundancy and backup of the liquid-cooled cooling water system, which is an economic solution to promote the transformation of existing machine rooms into liquid cooling.
4. Conclusion
At present, our country's digital economy is booming, especially the exploration and application of new technologies such as 5G, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things, which has promoted the rapid development of the data center industry, especially the deployment of high-power servers. This paper analyzes and summarizes the design and application of single-phase immersion liquid cooling system, including coolant and cooling water system, new and old data center computer rooms, and draws the following conclusions:
1) The characteristics of the immersion liquid cooling system and the differences from the traditional chilled water scheme are analyzed, and the key points that need to be paid attention to in the design of immersion liquid cooling and HVAC are summarized.
2) Based on the practical experience of previous projects, the advantages and disadvantages of open and closed cooling towers as cold sources in liquid cooling systems are compared and analyzed, so as to provide targeted reference for subsequent applications.
3) Combined with the characteristics of the existing machine room to transform the liquid-cooled machine room, an economic scheme for the design of liquid-cooled cooling source system is proposed for the reference and discussion of practitioners in the industry.
Source: Data Center Infrastructure Operation and Management, Authors: Zhao Luping, Xie Hongming, Xu Mingwei, Zhao Yifeng
Disclaimer: The information shared in part of this official account comes from the collection and collation of the Internet, all text and picture copyright belongs to the original author, and only represents the author's personal views, has nothing to do with this site, the article is only for readers to learn and communicate, and please verify the relevant content by yourself, if the content of the article involves infringement, please contact the background administrator to delete.

