Introduction: There are generally three backup methods between the primary and standby data centers: hot standby, cold standby and active-active.


01. Hot preparation
In the case of hot standby, only the primary data center undertakes the user's business, and the backup data center makes real-time backup of the primary data center, and when the primary data center is hung up, the backup data center can automatically take over the business of the main data center, and the user's business will not be interrupted, so the data center switching is not felt.
02. Cold preparation
In the case of cold standby, only the primary data center is responsible for the business, but the standby data center will not perform real-time backup of the main data center, which may be periodically backed up or not backed up at all, if the primary data center is hung up, the user's business will be interrupted.
03. Double active

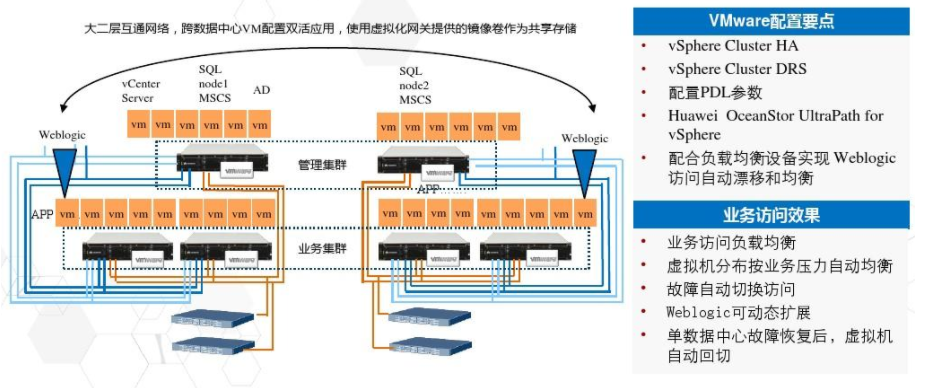
A—P
AP Active-Active classifies services into data center A and data center B as hot standby, while some services are based on data center B and data center B is hot standby to achieve the effect of approximate active-active.
A—A
AA active-active is truly active-active, and all I/O paths of the same active-active LUN can be accessed simultaneously, and the service load is balanced and can be seamlessly switched in case of failure.
04. What is an active-active data center?
First of all, we need to know that active is Active-Active, so the name implies that both sides provide services online with activities, which is relative to the traditional active-standby mode of Active-Standby mode. A true active-active solution should cover all levels of infrastructure, middleware, and applications.
The two data centers are peer-to-peer, regardless of master and slave, and can deploy services at the same time, which can greatly improve the utilization of resources and the work efficiency and performance of the system, so that customers can get the greatest value from the disaster recovery system.
a. The same business system is deployed in two production centers, and the load balancing technology of the network layer, host layer or application is combined to realize the parallel work and load sharing of the business system in the two data centers.
b. Two production centers deploy different business systems to take over each other's disaster recovery in real time.
Data center active active is divided into: active active in the same city and active active in different places.
Disadvantages of traditional primary/standby mode
For disaster recovery purposes, two (or more) data centers are generally built. One is the primary data center used to undertake the user's business, and the other is the backup data center is used to back up the data, configuration, and services of the primary data center.
There are generally three backup methods between the primary and standby data centers: hot standby, cold standby, and active-active.
● In the case of hot standby, only the primary data center undertakes the user's business, at this time, the backup data center makes real-time backup of the primary data center, when the primary data center is hung up, the standby data center can automatically take over the business of the main data center, and the user's business will not be interrupted, so the data center switching is not felt.
● In the case of cold standby, only the primary data center is responsible for the business, but the standby data center will not perform real-time backup of the main data center, which may be periodically backed up or not backed up at all, if the primary data center is hung up, the user's business will be interrupted.
● Active thinks that it is too wasteful to only do backups in the standby data center, so let both the primary and standby data centers undertake the user's business at the same time. Generally speaking, the load of the primary data center may be higher, such as sharing 6070% of the business, and the backup data center only sharing 40% or 30% of the business.
The traditional primary-standby mode is a service that only runs in one data center, and the enterprise deploys a large number of backup servers in the backup center based on the requirements of disaster recovery level and business requirements, but the backup center only provides disaster recovery services for the service.
Benefits of active-active data centers
Make the most of resources and avoid waste caused by a data center being idle all year round. Through resource integration, the service capacity of the "active-active" data center is doubled.
If one data center is disconnected and the other data center is still running, it is imperceptible to users.
In the mode of a disaster recovery center, if the production data center is paralyzed, it will take half an hour, even two hours, or even longer to start the disaster recovery center, and user transactions will be seriously damaged during the time when the disaster recovery center is started.
The biggest advantage of active-active data centers is the efficient use of resources. If the resources are idle, the resources are quite wasted, and with virtualization, the idle resources can be integrated, and the service capacity will be doubled. Many resources in the banking system are flexible demands, such as funds, precious metals trading, electronic payments, and online banking transactions, and the daily trading volume may reach the sum of the annual trading volume when trading is hot. Taking Taobao's "Double Eleven" event as an example, the transaction volume may reach the sum of the annual transaction volume in a few minutes, and the system service capacity needs to be increased tenfold. Cloud computing technology gives the IT system the ability to integrate resources, so that the system has full flexibility, and can dispatch ten machines at any time to improve service capacity to ensure the sudden demand for transactions, as well as the soaring transaction volume caused by various sudden factors.
With cloud computing technology, it does not mean that the investment will be less, but the resource utilization rate will be higher, the system will have stronger impact resistance, and the free scheduling ability will be stronger.
Automation is an essential prerequisite for "active-active" and "cloud computing"
Cloud computing requires automation to help system maintenance personnel carry out automatic resource provisioning. For example, tens of thousands of virtual machines are virtualized through virtualization technology, and 50 machines are needed to provide web services to the online banking system during the day, and there are fewer online banking transactions and more precious metal transactions at night, and these 50 machines need to be deployed to another system. It is impossible to deploy these fifty units one by one by one person, and they may not be able to be allocated overnight, so automated software is needed to automatically adjust resource allocation.
It is difficult to "double active" in different places
Of course, it is also very difficult to deploy "active-active" data centers, especially "active-active" in remote places, which involves data synchronization efficiency. If the data synchronization efficiency is not up to the requirements, it will cause a period of transaction loss in the event of a disaster. In the off-site "active-active" model, the data centers in the two places accept transactions at the same time, which is very technically difficult and requires many underlying programs to be changed.
There are three conditions for the construction of active-active data centers
The construction of an active-active data center must first meet three conditions, the first is application active, that is to say, the database must be active-active, the second is that the network must be active-active, the business network must ensure that the two data centers can be connected at the same time, and the third is that the data must be active-active, and the data on both sides must be able to be used independently.
Disadvantages of active-active data center solutions
Although the active-active disaster recovery solution ensures the linearity of business production to the greatest extent for centrally managed data centers, it effectively defends against catastrophic events and recovers business production. However, there are still certain shortcomings in the disaster recovery solution of active-active data centers, and there is always a certain distance between ideal and reality.
1. Cerebral split phenomenon
The active-active data center solution realizes a redundant disaster recovery solution at the site level, but is limited by the current technology and other factors, which solves the current business continuity problem faced by the enterprise in the construction process, and also creates a new problem, that is, the common split-brain phenomenon of the active-active solution. It makes it difficult for users to choose between which is the only production data and which is the non-production data that will be scrapped. This is one of the reasons why veritas VVR solutions were withdrawn from the disaster recovery arena in the early years.
2. It is not "zero loss", and there is no guarantee of soft errors
The advantages of active-active disaster recovery solutions emphasize that under a healthy operating platform, large-scale disaster events can cause "zero" data loss, but if the active-active platform itself is unhealthy or encounters logical failures, it cannot guarantee zero data loss. In the case of data recovery or gradual disaster in the event of such a failure, it is also necessary to use the data recovery method or method of the backup system. Therefore, active-active disaster recovery solutions do not have the guarantee of resolving soft errors in most cases, and the probability of such events far exceeds that of site-level disasters and hardware failure events. In 2012, a provincial government department's business system had built a disaster recovery system, but an error occurred when the business system was upgraded, resulting in business downtime for more than a week, and most of the time during this period was to find the basis for recovery data.
3. High reliability and performance degradation should be tolerated
Although the active-active disaster recovery solution improves site-level redundancy protection, it does reduce the reliability and performance of the overall service platform in practice. Whether it is a traditional cluster system, virtualized host platform Vmware, or Oracle RAC, etc., cross-site construction will invisibly add some unstable factors to the business platform. In terms of performance, the network latency of inter-site monitoring and synchronous confirmation of service sessions, as well as the optical fiber latency of data synchronization and double write, all affect the overall service processing performance to a greater or lesser extent. The farther the distance, the more obvious the impact, and if the distance is closer, the significance of building an active-active disaster recovery data center will also be lost.
4. Operation and maintenance are not simple
In addition to requiring enterprise users to improve their maintenance capabilities, they also need the after-sales service capabilities of active-active disaster recovery solution providers.
a. The maintenance ability of the enterprise's own personnel must be strengthened in order to have the ability to maintain the cross-site active-active system, that is, the maintenance personnel of the enterprise users themselves must change from the ability to maintain the equipment to the ability to maintain the active-active system architecture, in order to maintain the normal operation of the system and achieve the desired effect.
b. The service capabilities of the provider also directly affect the effect of the active-active disaster recovery system after deployment, in the existing cases, we often see the provider's 800 calls, in addition to collecting logs or collecting logs, in addition to being diagnosed in the background or in the background, often a small problem needs to be solved by many layers and times of communication, how to ensure the stability of the active-active disaster recovery system? How to ensure that the user's expectations for the linearity requirements of the active-active system are met?


5. The cost performance is not too high
We often hear that active-activity disaster recovery solutions can make both production centers and disaster recovery centers "live", effectively use resources, maximize the linearity of business systems in the face of catastrophic events, and eliminate the shortcomings of the original disaster recovery system. However, when we seriously considered building an active-active disaster recovery system, we found that if the maintenance capabilities of our IT personnel were insufficient, it would be difficult to achieve the desired results. In real cases, it is difficult for many users to apply for subsequent maintenance funds for the construction of the system at a one-time cost, which is difficult to effectively ensure the healthy operation of our information system. Bank of Ningxia is a major accident caused by hardware failure and human error in the repair process of its own IT personnel without the support of follow-up maintenance funds. Therefore, while building a dual-active disaster recovery system, it is necessary to ensure follow-up maintenance funds. The active-active disaster recovery system is shifted to a height.
If it is a global business, it will generally establish a global IDC in different regions, and establish at least 2 nodes in a region for master and standby or active-active.

